Well, we all know that in the past decade, healthcare has shifted from reactive treatment to proactive, data-driven engagement.
Patients now expect real-time access to health information and immediate support, something traditional systems often can’t deliver.
Having said that, the emergence of healthcare chatbots, a conversational AI capable of providing 24/7 AI patient scheduling, support, symptom triage, medication reminders, and administrative assistance.
Powered by natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning (ML), these systems are helping clinics and startups scale patient engagement at a fraction of the cost.
Whether it’s a virtual health assistant in telemedicine or a symptom checker chatbot for primary care, conversational AI is no longer an experiment; it’s a clinical necessity.
Key Takeaways
- PHI protection and encryption are the cornerstones of patient trust.
- Clinician escalation safeguards care quality and prevents harm.
- Ethical and explainable AI builds credibility and regulatory confidence.
- Integration with EHR and FHIR standards unlocks scalability.
- The best healthcare chatbots enhance clinicians — they never replace them.
What Is A Healthcare Chatbot?
A healthcare chatbot (also known as a medical chatbot or AI chatbot for healthcare) is an intelligent conversational system designed to simulate human dialogue in healthcare contexts.
It assists with everything from answering health-related queries to connecting patients with clinicians.
These bots can:
- Conduct symptom assessments using structured triage flows.
- Schedule and confirm appointments.
- Deliver personalized wellness advice and medication reminders.
- Help clinicians document visits and prepare patient notes.
- Integrate securely with EHR systems to update patient records automatically.
| Key Highlight: Chatbots like Ada Health, Babylon Health, and K Health have already proven that when paired with proper oversight and PHI-safe infrastructure, these systems can improve accessibility, reduce clinician burnout, and extend healthcare delivery to underserved regions. |
The Non-Negotiable Role of PHI-Safe Data Handling
Every healthcare interaction involves Protected Health Information (PHI), and protecting it isn’t optional.
PHI includes any information that can identify a patient, such as names, birthdates, lab results, and chat transcripts.
HIPAA, GDPR, and similar global regulations make it clear: mishandling PHI can destroy patient trust and expose organizations to massive penalties.
To safeguard PHI, follow these best practices:
- Encrypt everything. Use AES-256 for data at rest and TLS 1.3 for transmission.
- Limit access. Only authorized roles should handle PHI, enforced via RBAC and MFA.
- Log every event. Maintain immutable audit trails of access and data use.
- Minimize collection. Gather only essential data and anonymize when possible.
- Establish BAAs. Ensure all vendors (e.g., hosting or NLP providers) sign Business Associate Agreements for shared liability.
Soft Advice: Building a PHI-safe chatbot isn’t just about compliance; it’s about long-term credibility. In digital health, trust is your ultimate brand equity.
| Best Practice | Description / Implementation | Example Tools or Methods |
| Encrypt Everything | Use AES-256 for data at rest, TLS 1.3 for transmission | AWS KMS, Azure Key Vault |
| Limit Access | Apply role-based access control (RBAC) and MFA | Okta, Auth0 |
| Log Every Event | Maintain immutable audit trails | Splunk, CloudTrail |
| Minimize Collection | Store only essential data, anonymize when possible | De-identification pipelines |
| Establish BAAs | Ensure shared vendor liability | AWS, Microsoft, or Google Healthcare Cloud |
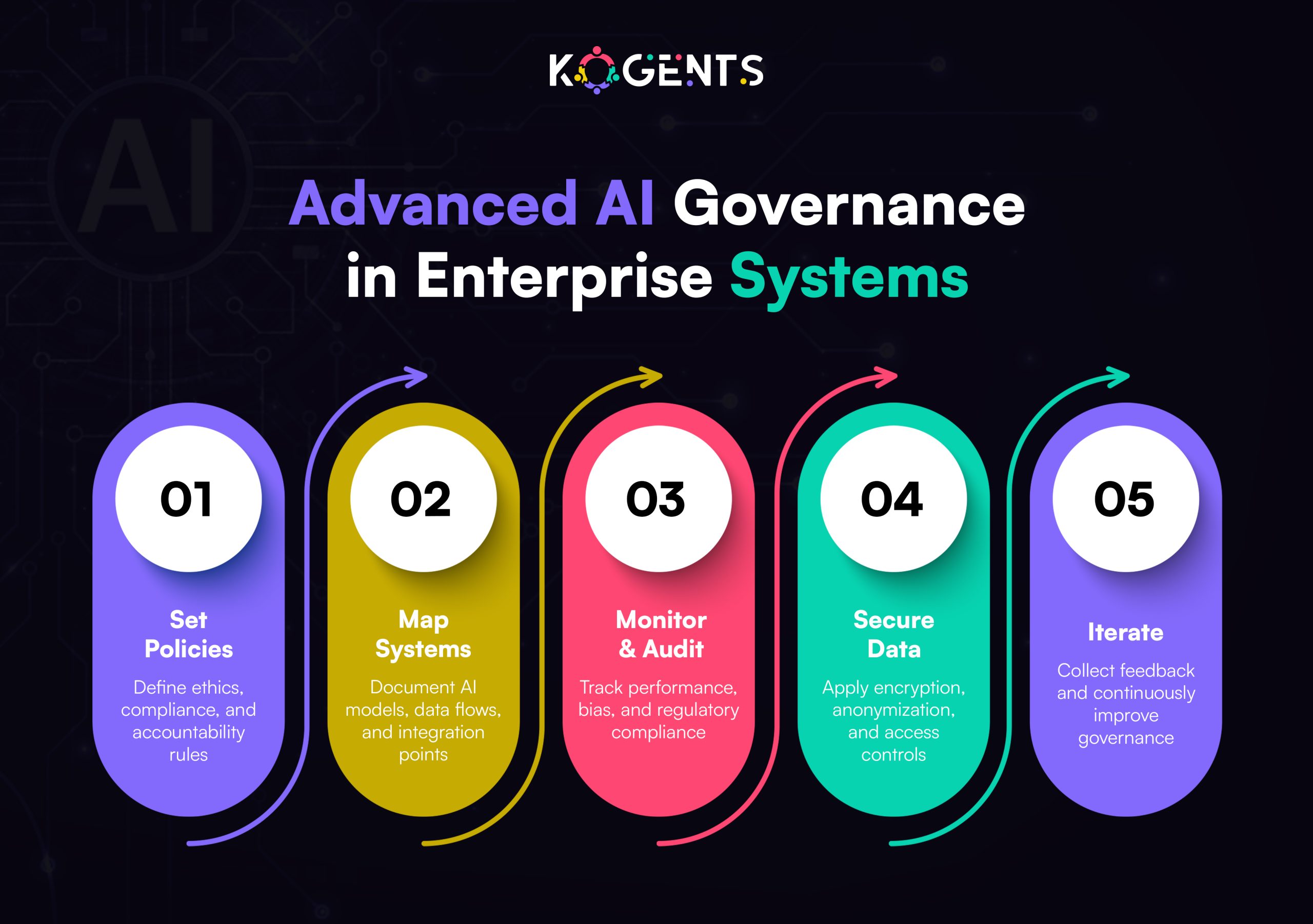
Architecting a Secure and Compliant Healthcare Chatbot
Think of your healthcare chatbot architecture as a fortress: every layer must defend patient privacy and clinical integrity.
The system typically includes:
- User Interface (UI): Web or mobile front-end with HTTPS encryption and consent prompts.
- NLP/AI Engine: Interprets user queries through intent recognition and entity extraction.
- Clinical Logic Module: Encodes triage protocols, guidelines, and escalation triggers.
- Integration Layer: Connects securely with EHR, FHIR, or HL7 systems.
- Security Layer: Encrypts data, authenticates users, and logs every transaction.
- Clinician Escalation Layer: Detects uncertainty or risk and transfers the conversation to human professionals.
Clinician Escalation: The Human-in-the-Loop Safety Net
A chatbot, no matter how advanced, must know its limits and when to escalate to a clinician.
| Case In Scenario: When a patient types “I’m dizzy and my heart hurts,” the chatbot should not attempt self-diagnosis. Instead, it should automatically route the case to a licensed clinician through a secure communication channel. |
The escalation workflow looks like this:
- Risk Detection: NLP identifies high-risk keywords or emotional distress cues.
- Confidence Threshold: If confidence falls below a set level (e.g., 70%), escalation triggers.
- Routing: The chatbot securely forwards the case to an on-call clinician.
- Human Oversight: A provider takes over, ensuring patient safety.
- Audit Trail: Every action is recorded for compliance review.
This hybrid model, combining AI triage with clinician escalation, reflects the philosophy behind AI ethics in healthcare: automation should support, not replace, human judgment.
Designing Ethical and Trustworthy Conversations
Ethical design is the foundation of trustworthy healthcare AI. The World Health Organization (WHO) and European Commission AI Ethics Framework both emphasize transparency, fairness, and accountability as guiding principles for all medical chatbots.
Here’s how to apply them:
- Transparency: Make it clear that users are talking to a chatbot, not a clinician.
- Consent: Always ask permission before storing or processing PHI.
- Empathy: Train the chatbot’s tone for compassion, especially for mental health contexts.
- Accessibility: Ensure the chatbot supports multiple languages and adheres to WCAG accessibility standards.
- Explainability: Use Explainable AI (XAI) techniques so clinicians understand why a chatbot recommended an action.
| Example:
“I’m your virtual health assistant. I can help you track symptoms, but I’m not a doctor. If your condition seems serious, I’ll connect you with a licensed professional.” |
Integrating Chatbots into Clinical and Business Workflows
For healthcare entrepreneurs, integration is where AI becomes ROI.
- In clinical settings, chatbots can automate patient intake, schedule follow-ups, verify insurance, and update records in real time.
- In business operations, AI agents for healthcare automation can manage customer support, streamline workflows, and handle repetitive queries that previously required staff.
- Imagine a small clinic that deploys a virtual medical assistant capable of answering basic patient questions, collecting vitals, and updating the EHR.
- For solopreneurs, this scalability is even more impactful. A mental health coach, for instance, can use a digital health assistant to monitor client progress, send reminders, and even check in automatically after sessions, all within a compliant, secure ecosystem.
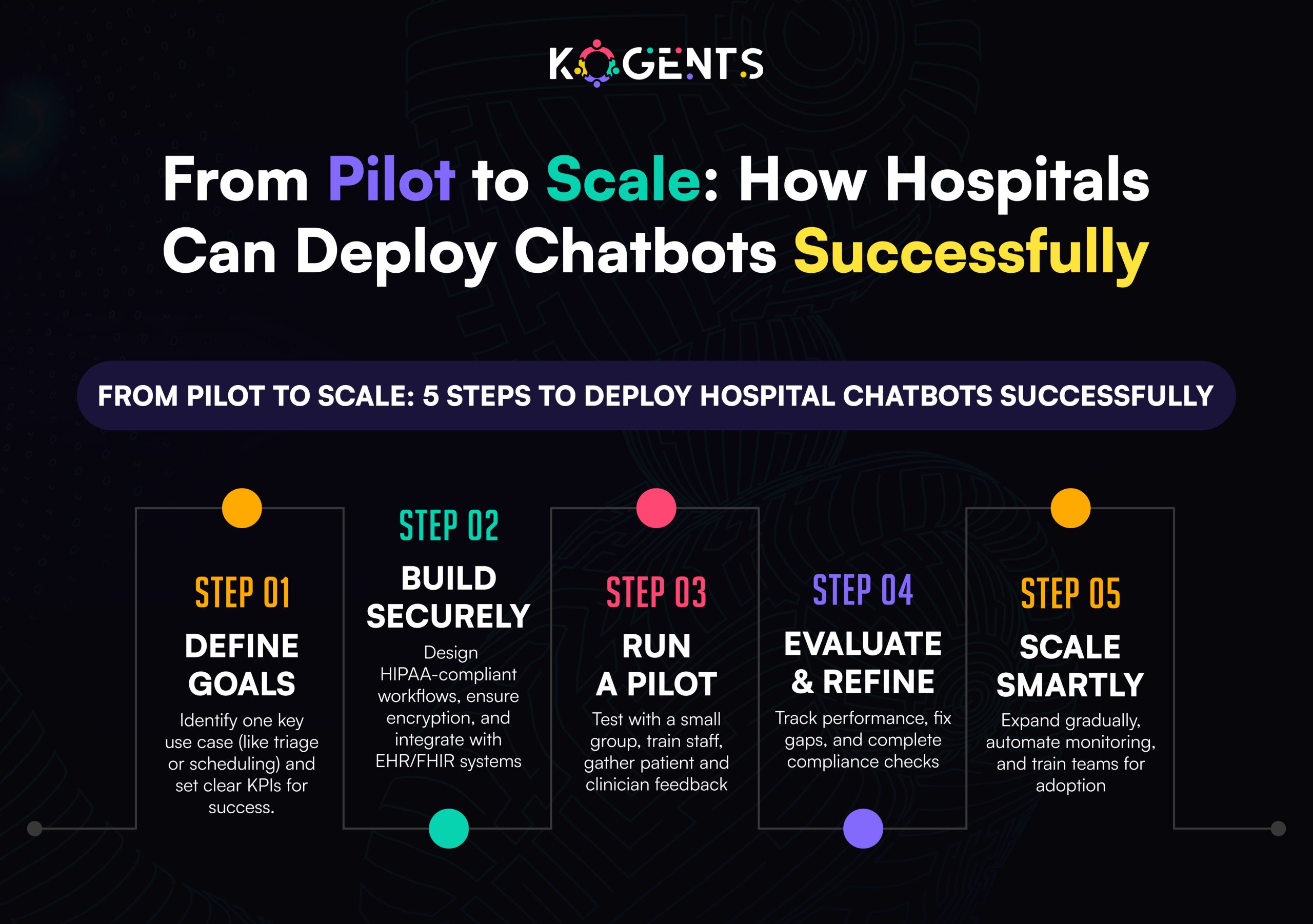
From Prototype to Production: The Deployment Roadmap
A great idea means little without a disciplined deployment process. Here’s a roadmap to move from concept to compliant launch.
- Define the Purpose. Choose a clear focus, triage, mental health support, or chronic disease management.
- Secure Infrastructure. Host on a HIPAA-compliant cloud such as AWS HealthLake or Microsoft Azure for Healthcare.
- Compliance Audit. Conduct internal HIPAA/GDPR assessments and draft BAAs with all vendors.
- Model Training. Fine-tune NLP models on de-identified medical data for accuracy and fairness.
- Testing. Simulate diverse user scenarios with clinician feedback loops.
- Pilot Launch. Start with a small user base; measure engagement, safety, and escalation success.
- Monitor Continuously. Establish a DevSecOps pipeline for ongoing updates, penetration testing, and PHI audits.
Remember: in healthcare AI, deployment isn’t the finish line; it’s the start of an ongoing safety commitment.
Real-World Use Cases
- Telehealth Providers use chatbots for patient screening before virtual appointments.
- Clinics deploy chatbots to manage scheduling, intake, and feedback collection.
- Mental Health Platforms rely on conversational agents for journaling and emotion tracking.
- Pharmacies integrate chatbots to help patients with refill reminders and side-effect reporting.
- Insurance Companies use bots to guide users through claims and benefits questions.
Challenges & Limitations
Building a PHI-safe healthcare chatbot comes with challenges that extend beyond coding:
- Data Breaches: Even small configuration errors can leak PHI. Continuous security audits are essential.
- Bias & Fairness: AI must be trained on diverse datasets to avoid discrimination in triage results.
- Regulatory Complexity: Laws evolve quickly — e.g., upcoming FDA AI/ML Action Plan updates.
- Clinician Resistance: Staff adoption depends on transparency and clinical value.
- Ethical Grey Zones: Mental health AI must tread carefully around AI doctor diagnosis and crisis intervention.
The Future: Hybrid Intelligence in Digital Health
Tomorrow’s healthcare chatbots will do far more than text-based conversations.
They’ll interpret voice, biometrics, and sensor data; interact across languages; and collaborate in real time with care teams.
Emerging trends shaping this future include:
- Multimodal AI combining text, speech, and imagery for richer diagnostics.
- Federated learning that improves model performance across hospitals without sharing PHI.
- Voice-enabled virtual assistants for aging populations.
- Proactive health management powered by wearable data integration.
- AI governance dashboards to monitor fairness and safety metrics continuously.
Case Study: MedConnect AI
MedConnect AI, a 2024 startup, launched a HIPAA-compliant healthcare chatbot for rural clinics.
The platform integrated FHIR APIs for EHR access, used AES-256 encryption, and featured built-in clinician escalation for symptom triage.
Within six months, results were dramatic:
- Average triage time dropped from 7 minutes to 2.
- Clinician workload decreased by 35%.
- PHI breach rate = 0.
- Patient satisfaction rose to 93%.
MedConnect’s founders, both solopreneurs, proved that responsible design and clinician collaboration can make AI both ethical and profitable.
Responsible AI is the Future of Healthcare!
Deploying a PHI-safe healthcare chatbot is not merely a technological achievement; it’s a statement of ethical commitment and trust.
When an entrepreneur designs with privacy in mind, clinicians engage confidently, and patients share openly.
When human oversight is embedded into automation, care becomes not only faster but safer. And when startups align with regulations from HIPAA to GDPR, they don’t just comply — they lead.
Ultimately, a successful healthcare chatbot isn’t measured by its sophistication, but by its compassion, security, and reliability.
These three pillars — privacy, empathy, and clinical escalation- define the difference between a tool that chats and one that truly cares.
If you’re ready to deploy AI that patients and providers can trust, now is the time to act. So, get in touch with the team at Kogents.ai to build secure, compliant, and human-centered AI systems. Call us at +1 (267) 248-9454 or drop an email at info@kogents.ai.
FAQs
What is a healthcare chatbot, and how is it used in clinics?
A healthcare chatbot is an AI-powered conversational system that assists patients and clinicians through natural dialogue. It’s used for appointment booking, symptom triage, medication reminders, and health education — improving accessibility and efficiency.
How can I ensure my healthcare chatbot is HIPAA-compliant?
To be HIPAA-compliant, encrypt all PHI using AES-256 and TLS 1.3, use access controls with multi-factor authentication, maintain audit trails, and ensure vendors sign BAAs. Regular third-party security audits are also essential.
What is PHI-safe data handling, and why does it matter?
PHI-safe handling ensures patient data is protected from unauthorized access or misuse. It’s vital because breaches can lead to regulatory fines and loss of patient trust. Proper encryption, data minimization, and anonymization safeguard privacy.
How does clinician escalation work in healthcare chatbots?
Clinician escalation activates when the AI detects risk or uncertainty — for example, when a user reports severe symptoms. The chatbot transfers the case to a licensed clinician through secure systems, ensuring timely and safe intervention.
Are AI chatbots replacing doctors or nurses?
No. AI chatbots are designed to support healthcare professionals, not replace them. They handle repetitive or low-risk tasks, allowing clinicians to focus on high-value care that requires human judgment and empathy.
What technologies power a modern healthcare chatbot?
These bots use natural language processing (NLP), machine learning, LLMs, FHIR API integration, and encryption frameworks. Tools like Microsoft Azure for Healthcare or AWS HealthLake provide HIPAA-ready infrastructure.
What are the most common healthcare chatbot use cases?
Top use cases include symptom triage, appointment scheduling, chronic disease management, mental health support, and patient education. Startups also use chatbots for intake automation and remote monitoring.
How can startups deploy a chatbot safely without a large team?
Entrepreneurs can leverage pre-certified cloud services (AWS, Azure) with HIPAA compliance built in, use no-code bot builders that support FHIR integration, and outsource compliance audits to third-party firms specializing in healthcare AI.
What are the biggest risks in deploying a healthcare chatbot?
Risks include PHI breaches, algorithmic bias, hallucinated medical advice, and poor clinician integration. These can be mitigated through human-in-the-loop escalation, regular model retraining, and strict data governance.
What’s the future of AI chatbots in healthcare?
The next generation of healthcare chatbots will be multimodal, combining voice, vision, and predictive analytics. They’ll proactively alert clinicians to health risks and work as co-pilots in clinical care — blending automation with empathy.