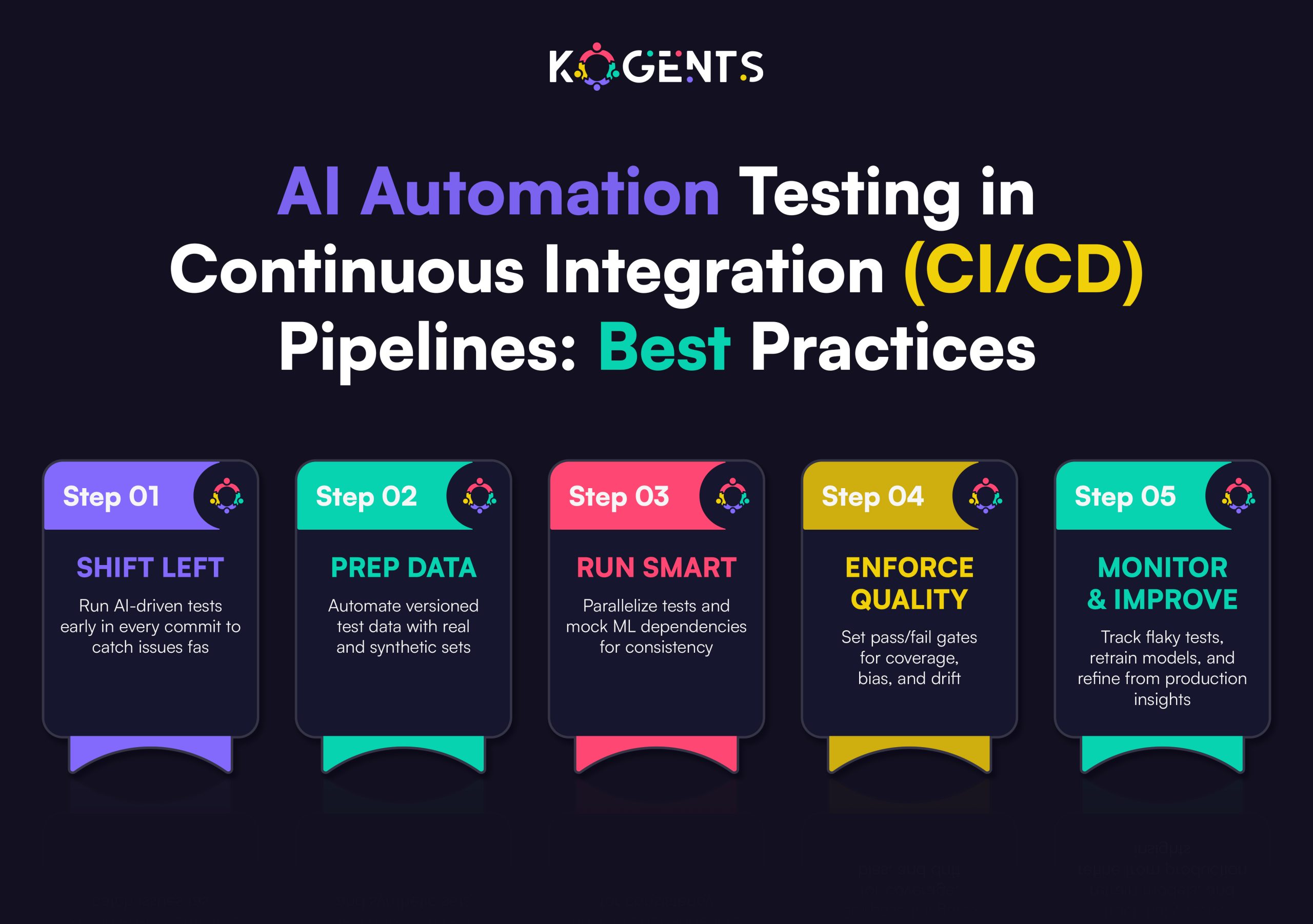
The business industry is growing faster than ever before. Every organization, from small startups to large enterprises, is on a journey toward automation and digital transformation.
In the core of this revolution lies workflow automation, a process that is drastically improving operational efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and productivity.
But what truly sets this era apart is the integration of AI agents in automating workflows.
As businesses strive to enhance their performance, AI-powered workflow automation is at the forefront, helping enterprises achieve smoother operations and smarter decision-making.
This blog explores real-world workflow automation examples in modern enterprises, showcasing how AI agents are redefining business processes across industries.
Key Takeaways
- Workflow automation AI agents improve efficiency by reducing manual tasks and human error.
- Automation frees up human resources to focus on high-value work.
- Industries such as finance, healthcare, and logistics have successfully implemented AI-driven workflows.
- Popular tools like Zapier, Microsoft Power Automate, and UiPath are key players in workflow automation.
- The future of business process automation includes enhanced AI, machine learning, and cloud-based solutions.
Comprehend Workflow Automation in Business
It refers to the use of technology to streamline repetitive tasks and business processes.
By eliminating manual efforts, it ensures that workflows run more efficiently, allowing employees to focus on value-adding activities rather than getting bogged down with mundane tasks.
However, when businesses layer AI agents over these workflows, the automation becomes significantly more intelligent.
Artificial Intelligence brings an element of decision-making and predictive capabilities to automation, allowing workflows to adapt and evolve based on changing data and conditions.
In the past, business workflows were automated through simple rule-based systems.
But with the introduction of machine learning (ML) and AI, businesses can now automate complex processes, from customer service interactions to inventory management, in ways that go beyond basic task repetition.

Workflow Automation Examples in Action
1. Automating Customer Support with AI Agents
One of the most common business process workflow automation use cases is the integration of AI in customer service operations.
AI-driven chatbots are transforming how businesses interact with customers.
These bots can manage inquiries, resolve complaints, and guide users through troubleshooting, significantly reducing the need for human intervention.
Example: Zendesk and Intercom leverage AI to automate ticket management, leading to fast response times and improved customer satisfaction.
2. Financial Services: Streamlining Invoice Processing
In the finance industry, AI agents play a critical role in automating the approval process for invoices and payments.
Platforms like Kofax and ABBYY use AI and Optical Character Recognition (OCR) to extract data from invoices, categorize it, and approve payments based on pre-set business rules.
Soft Reminder: This reduces the chance of human error and accelerates the approval process, making it far more efficient.
3. AI in Human Resources: Streamlining Recruitment
HR departments can benefit significantly from workflow automation processes powered by AI.
Companies like HireVue use AI to evaluate candidate interviews and rank them based on their answers and facial expressions.
Automated applicant tracking systems like Workday also streamline the hiring process by filtering resumes and automating candidate communications, freeing up HR professionals to focus on more strategic tasks.
4. Healthcare: Automating Patient Management
In the healthcare industry, AI-driven workflow automation is transforming patient management systems.
Example: AI agents can schedule appointments, send reminders, and even prioritize cases based on urgency.
Systems like Cerner and Epic Systems are integrating automation to manage patient data, reducing administrative workloads and improving the quality of care.
5. Sales and Marketing Automation
Sales and marketing teams also use AI for workflow optimization.
By integrating AI with tools like HubSpot or Marketo, businesses can automate lead generation, scoring, and nurturing.
Automated decision-making processes help ensure the right content reaches the right audience at the right time, optimizing conversions and improving ROI.
Comparison of Popular Workflow Automation Tools
| Tool | Features | Best For | Pricing |
| Zapier | Connects 2,000+ apps, automates tasks | Small to medium businesses | Free & Paid Plans |
| UiPath | RPA, AI decision-making, integrations | Large enterprises | Custom Pricing |
| Microsoft Power Automate | Automates Office workflows, integrates with MS apps | MS-centric businesses | Subscription-based |
| Monday.com | Task management, automation templates | Teams, HR, project management | Subscription-based |
Case Studies: AI Workflow Automation in Action
Case Study 1: Unilever’s Global HR Transformation
Unilever, a global leader in consumer goods, implemented AI-powered workflow automation in its HR operations to manage employee engagement, recruitment, and learning.
Result: By automating many HR processes, Unilever saved significant time and resources while increasing employee satisfaction.
The company’s AI-driven platform now manages repetitive tasks such as payroll and benefits administration, improving the overall efficiency of the HR department.
Case Study 2: Deloitte’s Financial Services Automation
Deloitte, one of the largest professional services firms, leveraged RPA and AI to automate financial services workflows.
Outcome: By integrating intelligent bots into their processes, it was able to drastically reduce the time spent on tasks such as data entry and reconciliation, allowing employees to focus on higher-value activities like financial analysis and consulting.
Case Study 3: ERP Finance Automation — “FinRobot” Framework
Another academic study described a framework called “FinRobot: Generative Business Process AI Agents for Enterprise Resource Planning,” focused on the finance/ERP domain.
Context & challenge:
- Large financial institutions rely on ERP systems, but these often depend on static workflows, manual inputs, and rigid rules.
- The need: scale to complex workflows (e.g., budget planning, wire transfers, financial reporting) involving both structured and unstructured data, real‑time changes, and dynamic decision logic.
Solution:
- The researchers proposed an AI‑native agent‑based framework (Generative Business Process AI Agents / GBPAs) that can reason, interpret user intent, orchestrate sub‑agents, and synthesise workflows on the fly.
- Example workflows: (a) employee reimbursements, (b) bank wire transfers — where the system handled tasks end‑to‑end with minimal human hand‑offs.
Results:
- Up to 40% reduction in processing time.
- Up to 94% drop in error rate.
- Improved regulatory compliance via built‑in semantic reasoning and risk control insertion.
Case Study 4: Healthcare Revenue Cycle Automation — Omega Healthcare Management Services + UiPath
A widely covered industry example: Omega Healthcare (a large revenue‑cycle‑management firm supporting 350+ healthcare organisations, 30,000+ employees) used UiPath’s AI‑powered Document Understanding tool to automate administrative workflows.
Context & challenge:
- Omega processes ~250 million transactions a year (medical billing, insurance claims, documentation).
- Manual tasks were high volume, error‑prone, and slow.
The goal: move from manual, repetitive work to decision‑based human roles, accelerating turnaround, improving accuracy.
Solution:
- UiPath’s AI‑Document Understanding tool extracted data from various documents (accounts receivable correspondence, insurance denial letters, and medical records).
- Automated large portions (60‑70% of clients’ tasks) of document‑processing workflows.
Results:
- Saved over 15,000 employee hours per month.
- Documentation time down by 40%.
- Turnaround time got cut by 50%.
- Accuracy reached 99.5%.
- Delivered 30% ROI for clients.
Why does it matter?
- This is a very high‑visibility “workflow automation in business”
Example: an enterprise uses AI agents + RPA for workflow optimisation in a high‑stakes domain (healthcare).
- It demonstrates the power of combining business process automation workflow + AI + workflow management in a real‑world enterprise scenario.
The Future of AI-Powered Workflow Automation
As the digital transformation landscape evolves, workflow automation solutions are becoming more sophisticated. Future trends show the continued rise of AI-powered solutions, including:
- AI-driven decision-making: More businesses are turning to machine learning models to make predictions and optimize workflow decisions based on historical data and emerging trends.
- Cloud-based workflow automation: With the growing adoption of cloud computing, businesses are shifting toward cloud-based platforms that provide more flexibility and scalability in automating workflows.
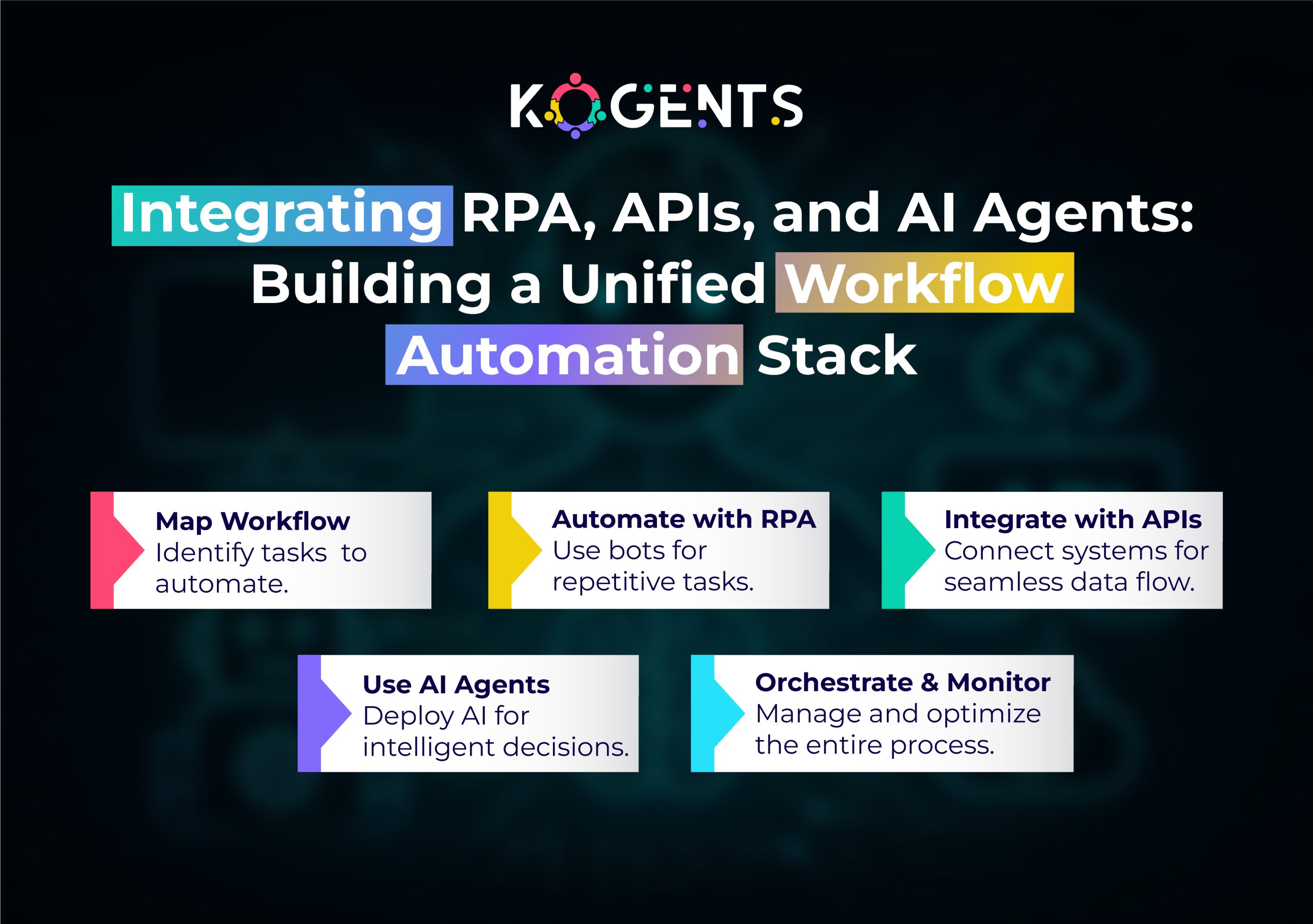
- Increased integration of AI and RPA: Combining Robotic Process Automation (RPA) with AI allows businesses to not only automate repetitive tasks but also make intelligent decisions based on data analysis.

Unveil The Power of Workflow Automation Powered by AI With Us!
Workflow automation examples powered by AI are not just about saving time; they are about transforming the way businesses operate.
By adopting AI agents into their workflows, companies can achieve unprecedented levels of efficiency, accuracy, and cost-effectiveness.
Whether automating customer support, invoice processing, or HR tasks, AI is revolutionizing how enterprises handle their day-to-day operations.
The future of business operations lies in automated decision-making and AI-powered workflow solutions.
With the continued growth of AI, RPA, and machine learning, businesses that embrace these tools will lead the charge in their respective industries.
The time to adopt automation is now. So, contact the team at Kogents.ai, and give your business the edge to act quickly in reaping the rewards.
FAQs
What are some real-world examples of workflow automation?
Some notable examples include automating customer service with chatbots, invoice processing in finance, and recruitment in HR departments.
What are the benefits of AI in workflow automation?
AI enhances workflow automation by making processes more intelligent, improving decision-making, and optimizing workflows based on historical data and real-time conditions.
How do workflow automation tools work?
Workflow automation tools use algorithms and pre-set rules to automate tasks, integrate with existing software, and eliminate the need for manual intervention.
How can businesses implement workflow automation?
Businesses can implement workflow automation by identifying repetitive processes, selecting the right tools (like Zapier, UiPath, or Microsoft Power Automate), and integrating AI for intelligent decision-making.
What industries benefit most from workflow automation?
Industries like healthcare, finance, retail, and human resources benefit immensely from AI-driven workflow automation.
What is Robotic Process Automation (RPA)?
RPA is a technology used to automate repetitive, rule-based tasks using robots or “bots” that mimic human actions.
Is AI-driven workflow automation expensive?
The cost depends on the scale and complexity of the business’s needs. However, many affordable tools and solutions are available for small and medium-sized businesses.
How do I choose the right workflow automation tool?
The right tool depends on your business needs, budget, and existing software ecosystem. Tools like Zapier are great for small businesses, while UiPath and Automation Anywhere are suited for larger enterprises.