In the high-velocity world of customer relationship management, every second counts. For organisations running the Salesforce CRM platform, the promise is always the same: turn data into action, turn action into relationships, and turn relationships into revenue.
But to truly optimize performance, you need more than CRM; it demands bold automation at every step in the workflow.
That’s where workflow automation in Salesforce meets AI-powered intelligent agents. Imagine tasks like lead distribution, approval routing, or case escalation happening without human hand-off, guided by real-time insights and machine intelligence.
The result: a leaner, faster, and smarter CRM engine.
In this post, we’ll dive deep into how to integrate AI-driven agents with Salesforce workflow automation examples and real-world cases to transform the business process automation environment.
Key Takeaways
- Workflow automation on the Salesforce platform is no longer optional; it’s essential to scale, shorten cycles, and reduce manual overhead.
- Intelligent agents embedded in Salesforce shift the focus from “doing tasks” to “making decisions”.
- Migrating from legacy workflow rules/process builder to Salesforce Flow and Flow Orchestrator is critical for future-proofing.
- The business impact is measurable: cost savings, productivity gains, improved customer & employee satisfaction.
- Governance, monitoring, and alignment between business processes and automation tools are must-haves to avoid chaos and technical debt.

The Big Picture: What Is Workflow Automation in Salesforce and Why Does It Matter?
Workflow automation in Salesforce uses built-in tools to trigger and execute business processes without manual effort.
It automates sales, service, marketing, and operational tasks, reducing delays and human error.
Commonly known as Salesforce process automation or Salesforce Flow, the goal remains the same: seamless, efficient workflows.
Automation ensures data moves accurately across teams and systems in real time. At scale, it evolves into enterprise-wide business process workflow automation powered by AI.
A well-automated Salesforce transforms the CRM from a data repository into an intelligent action engine.
The Evolution: From Legacy Workflow Rules to Declarative Tools, to AI-Powered Intelligent Agents
Legacy Tools
- Originally, Salesforce offered Workflow Rules and the Process Builder for automation.
- Workflow rules allow simple “if-this-then-that” triggers, when a record meets criteria, update a field, send an email, create a task.
- Process Builder extended this to allow branching logic and more actions.
Salesforce Flows are designed for complex, multi-step business processes.”
Declarative Tools: Flow & Orchestrator
- Stepping into Salesforce Flow and Flow Orchestrator. Flow allows admins to build more complex logic, user-input screens, loops, sub-flows integrations, all without code.
- Flow Orchestrator adds multi-stage, multi-user orchestration of flows, especially for processes that span departments, approvals, and branches.
AI & Intelligent Agents
- AI-powered agents take automation beyond triggers and actions, adding insight, prediction, and orchestration.
- They analyse data, route tasks smartly, suggest next steps, and handle exceptions in real time.
- In service operations, they triage cases, escalate issues, and guide agents with contextual insights.
- This marks the shift from simple workflows to intelligent, AI-driven orchestration for peak performance.
How Intelligent Agents + Workflow Automation Elevate Salesforce Performance?
Below are key capabilities:
Trigger–Condition–Action logic
- At the core of any workflow automation is a trigger (e.g., “Lead enters system”, “Opportunity stage changes”, “Case created with priority = High”), plus conditions (criteria/filter) and actions (field update, task creation, email, integration call).
- Using Flow Builder, admins set up these automations declaratively.
Example: assign lead to region rep when lead score > 80 and industry = “Manufacturing”.
Lead Routing Automation & Pipeline Automation
- For the sales team, automating the routing of leads (e.g., by geography, lead score, product interest) ensures faster follow-up and higher conversion.
- Likewise, pipeline automation in Salesforce ensures opportunity stages are advanced automatically based on criteria, or reminders/alerts are generated when deals stagnate.
Multi-Step Approvals & Service Case Escalations
- In service scenarios, multi-step workflows include intake → triage → action → resolution → escalate → close.
- Using Flow Orchestrator and intelligent agents, you can route cases dynamically based on customer tier, issue type, channel, or sentiment.
The “Salesforce service workflows” guide notes clear logic flows: “Inputs and triggers … Decision points … Stakeholders … Data flow and automation.”
Intelligent Agent Capabilities
- Next-Best-Action/Recommendation: AI analyses record history and suggests optimal next action (e.g., route this case to senior rep, escalate this opportunity, send renewal reminder)
- Predictive routing: intelligent agents analyse data to route tasks proactively.
- Automated follow-ups & reminders: ensure no lead or case falls through the cracks.
- Integration & seamless hand-off: workflow automation AI agents can integrate with external systems, API, or AI agents.
- Monitoring, exception handling & optimisation: Agents monitor workflow performance, alert when loops or bottlenecks occur, and suggest optimisations.
Data Model, Integration, and Governance
Performance optimization also requires solid underlying infrastructure: correct data model, clean duplicate rules, integration with ERP/other systems, API trigger orchestration, and governance around automation tools.
Example: Flow Orchestrator provides visibility into orchestration runs and bottlenecks.
Scalability & Enterprise Performance
When workflows are automated across thousands of records and multiple teams, manual errors decline, cycle times shorten, and the CRM becomes a proactive engine for the business—not just a passive database. The automation of Salesforce workflows enables this scale.

Feature Comparison Table: Legacy vs Modern vs AI-Powered Workflow Automation in Salesforce
Implementation Roadmap: Steps to Get Started
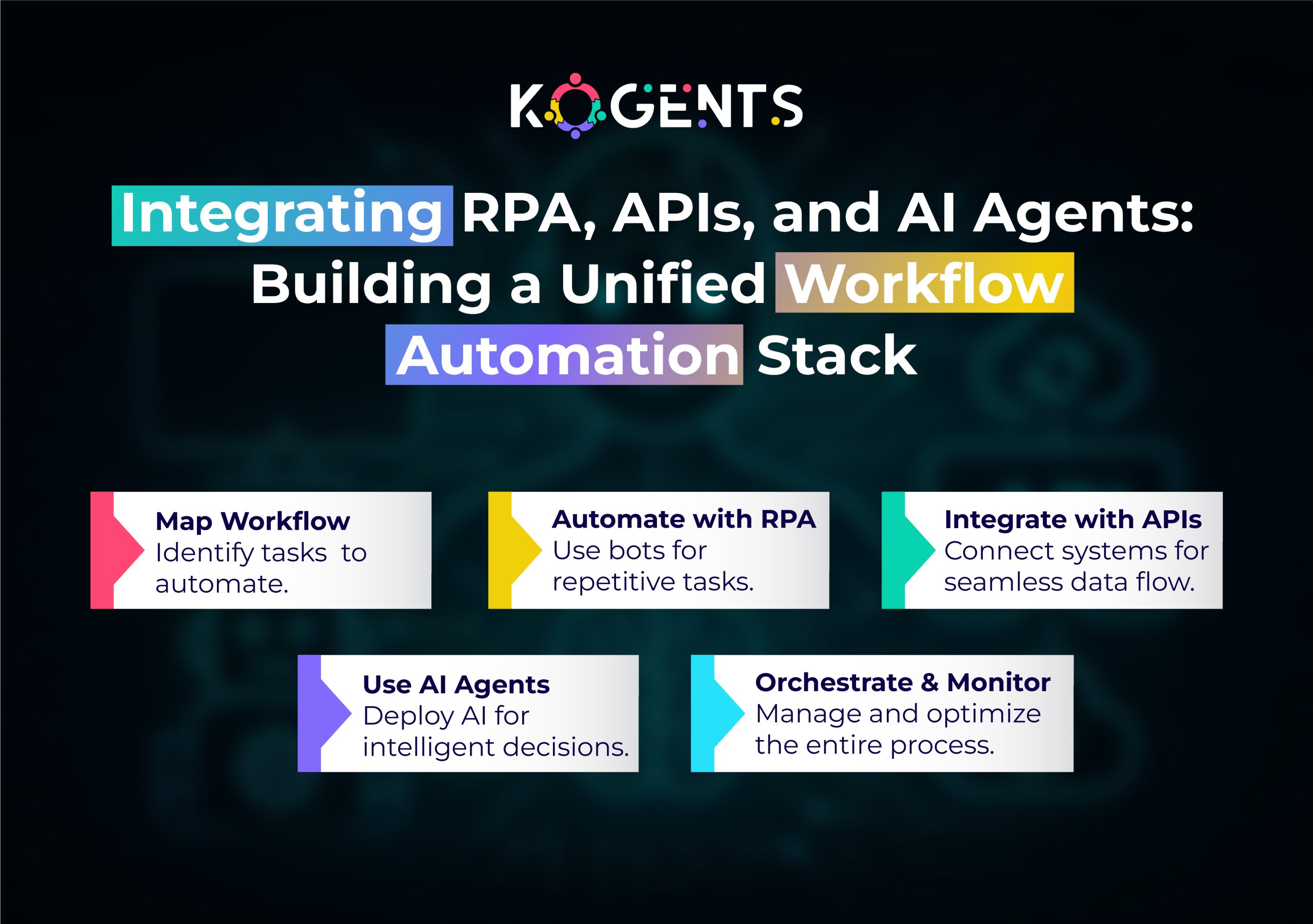
Here’s a structured approach to deploy workflow automation in Salesforce coupled with intelligent agents:
Step 1: Define your business process
- Map the end-to-end workflow (e.g., lead to opportunity, service case to resolution)
- Identify key triggers, decision points, participants, and outcomes
- Prioritise processes that will deliver high ROI.
Step 2: Choose the right automation tool
- For simple automations: Flow Builder
- For multi-step, multi-user, cross-departmental: Flow Orchestrator
- Ensure legacy Workflow Rules / Process Builders are migrated forward
Step 3: Incorporate intelligent agents & AI
- Use AI to analyse data and predict next steps.
- Build agents that monitor workflows, detect exceptions, trigger alerts,alerts optimize processes.
- Processes rate data from CRM, ERP, and external sources for deeper insight.
Step 4: Pilot & measure
- Build a pilot automation for one high-value process
- Measure key metrics: time saved, error rate, response time, conversion rate.
- Collect feedback from users and adjust.
Step 5.: Scale & govern
- Roll out automations across other processes
- Set up governance: change control, documentation, and a monitoring dashboard
- Establish a workflow library, versioning, and retire legacy automations
- Monitor continuously and optimise based on data
Step 6: Maintain & optimise
- Use agent insights to spot bottlenecks, loops, and underused processes.
- Review periodically: are the criteria still valid? Are decision trees efficient?
- Keep alignment with business strategy, processes evolve.
Case Studies: Real-World Success Stories
Case Study 1: SmartRent
SmartRent leveraged Salesforce’s automation capabilities to eliminate manual tasks and streamline processes, saving $300,000, increasing employee retention by 92%, and saving employees 120 hours in onboarding time.
Key learnings: By automating onboarding, SmartRent reduced repetitive tasks, improved employee experience, and freed up time for strategic activities.
Case Study 2: Multi-department Orchestration Example
One organisation used Flow Orchestrator to build a record-triggered orchestration for case management, involving multiple teams and actions.
Key learnings: This illustrates how workflow automation on the Salesforce platform spans users/departments, not just simple tasks. Orchestrator enabled complex flows, visibility, and fewer coding dependencies.
Case Study 3: IDC Industry Survey
Key learnings: These macro results underline large benefits when automating workflow, which applies to Salesforce workflows when executed properly.
Conclusion
Today, workflow automation in Salesforce, powered by AI agents, is key to agility and performance.
Automate lead routing, approvals, and service escalations with intelligent, predictive workflows.
Transform Salesforce from a static CRM into a dynamic growth engine.
So, do you want to achieve prompt cycles, fewer errors, happier teams, and measurable ROI?
Kogents.ai helps organisations design, integrate, and govern Salesforce automation.
FAQs
How does Salesforce workflow automation work in a CRM context?
Within the CRM, automation begins with a trigger (e.g., lead enters system), then evaluates conditions (e.g., region = APAC, score > 80), then performs actions (assign to rep, send notification, update field), often via Flow or Orchestrator. Intelligent agents may add prediction, routing suggestions, or alerts.
What is the difference between workflow automation using Salesforce Flow and legacy Workflow Rules / Process Builder?
Workflow Rules are simpler, limited to single-step actions. Process Builder introduces more branching. Salesforce Flow supports multi-step logic, user-input screens, loops, and integrations. Flow Orchestrator adds stages, multi-user orchestration. Legacy tools are being deprecated.
How can intelligent agents help in the automation of Salesforce workflows?
Intelligent agents bring AI capabilities: they can analyse past data, predict the best next action, route workflows dynamically, monitor bottlenecks, suggest workflow improvement, and escalate tasks proactively. This enhances automation from just “execute the action” to “make the decision”.
What is Salesforce Flow Orchestrator, and when should you use it for automation?
Salesforce Flow Orchestrator is the automation tool that supports building and orchestrating multi-step, multi-user, multi-stage business processes without code. Use it when a process spans multiple teams, stages, or has complex branching.
What pitfalls should I avoid when implementing Salesforce automation workflows?
Avoid: implementing without clear process mapping, automating too many ad-hoc tasks, neglecting documentation, ignoring data quality, failing to migrate legacy automation tools, having no governance or monitoring, and letting technical debt build.