Large universities today operate more like federated ecosystems than single institutions. They’re spread across multiple campuses, satellite centers, online environments, and hybrid learning frameworks.
Each campus has its own workflows, academic schedules, advising teams, IT infrastructure, and compliance nuances.
This fragmentation creates inequities in student support, uneven administrative efficiency, and inconsistent academic experiences.
Enter agentic AI in higher education, an evolution beyond traditional automation.
Unlike static systems, these are AI agents for Education capable of understanding context, reasoning across multiple datasets, and taking actions that mirror human judgment.
They function as intelligent collaborators, orchestrating processes across enrollment, advising, curriculum delivery, LMS workflows, academic administration, and student engagement.
But agentic AI is only powerful when governed correctly. Without safeguards, consistency collapses.
That’s why standardized AI governance protocols have become the backbone of multi-campus transformation.
The next-generation university doesn’t just use AI; it uses governed autonomous AI agents aligned with FERPA, GDPR, UNESCO AI ethics, EDUCAUSE Horizon frameworks, and the NIST AI Risk Management Framework to orchestrate decisions across campuses with precision, trust, and interoperability.
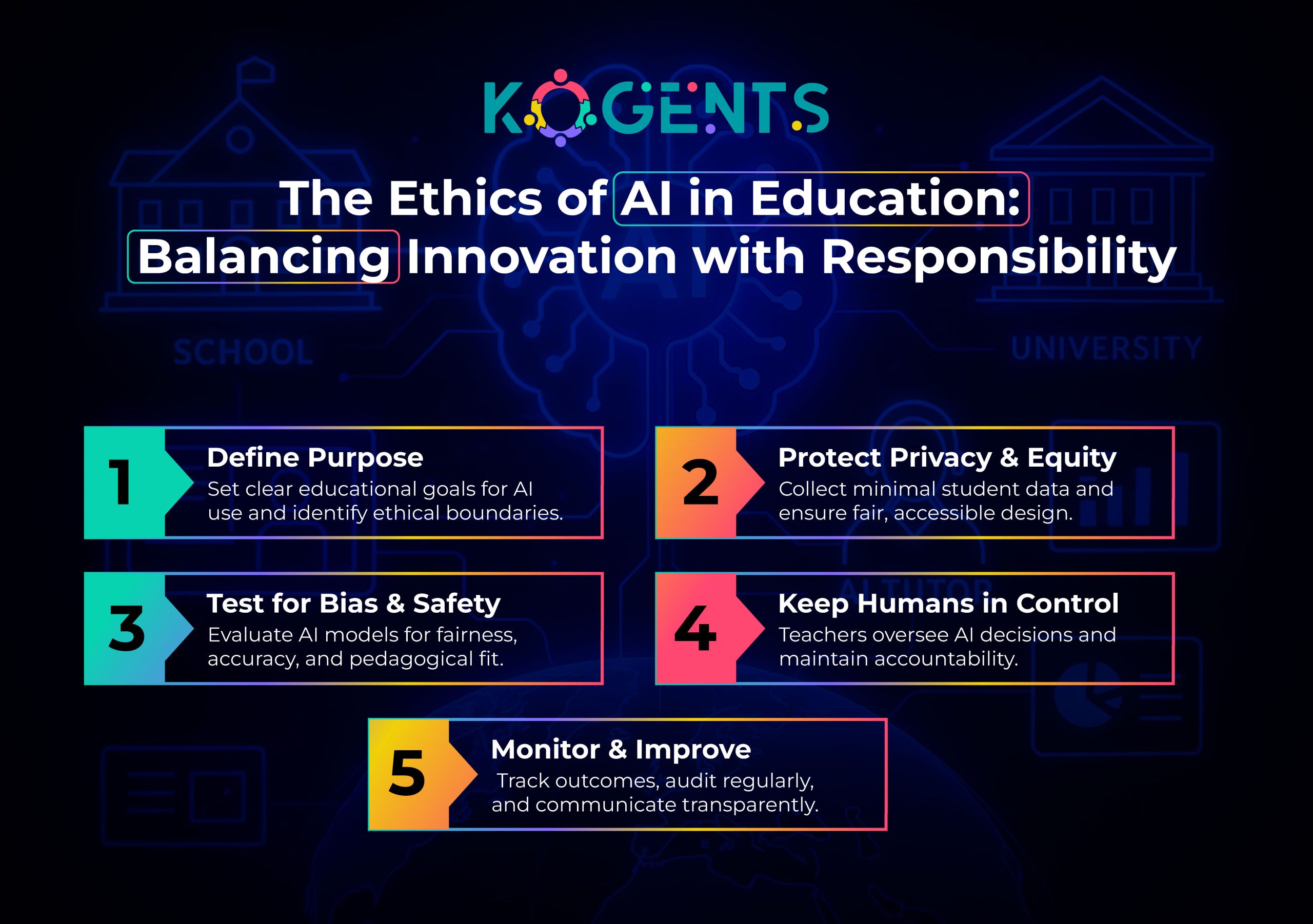
Key Takeaways
- Agentic AI is different from generative AI — it performs tasks autonomously, such as scheduling, advising, compliance monitoring, and multi-campus academic planning.
- Multi-campus universities benefit the most because agentic AI unifies fragmented workflows into a single intelligent operational layer.
- Standardized governance protocols ensure safety, transparency, and FERPA-aligned accountability, enabling AI decisions to remain consistent across all campuses.
- AI Agents for Higher Education improves student success and learning outcomes using adaptive learning systems, learning analytics, AI-driven advising, and predictive student success agents.
- Universities that implement agentic governance now will become future-ready institutions, able to scale operations, reduce costs, and improve academic integrity.
What Exactly Is Agentic AI in Higher Education?
At its core, agentic AI in higher education consists of intelligent, autonomous systems that perform actions independently, make context-aware decisions, and coordinate with other AI agents or human stakeholders.
These are not just chatbots or simple scripts; they represent a new paradigm in university operations.
Agentic AI includes:
- AI agents in higher education that analyze student records, recommend schedules, and triage advising needs.
- Autonomous AI agents for teaching & learning that adjust course materials and assessments in real time.
- AI-powered autonomous agents for learning that provide personalized learning pathways.
- Agentic learning systems in universities that dynamically adapt to learning styles, mastery levels, and outcomes.
- Intelligent academic workflow automation engines that streamline administrative processes.
Unlike traditional AI, which responds only when prompted, agentic AI:
- Perceives changing conditions
- updates its reasoning models
- collaborates with other agents
- Predicts student or operational needs
- triggers actions proactively
This means it can manage tasks like:
- Assigning students to optimal courses
- monitoring cross-campus resource use
- Adjusting LMS content difficulty
- executing compliance audits
- balancing faculty workloads
- predicting enrollment trends
This evolution represents a shift from reactive AI to proactive and autonomous AI, a monumental leap for multi-campus universities.
Why Multi-Campus Institutions Are the Perfect Environment for Agentic AI?
The complexity of running three, five, or even twelve campuses under one administrative umbrella is staggering.
Each campus operates semi-independently, resulting in:
- fragmented advising processes
- duplicated administrative tasks
- inconsistent academic policies
- uneven student support
- siloed data systems
- mismatched course schedules
- conflicting resource allocation
- localized compliance risk
Agentic AI solves these challenges by operating as an interconnected multi-agent system that governs processes uniformly while adapting to each campus’s unique variables.
Examples of AI in education are:
- A predictive enrollment management agent forecasts seat demands across all campuses simultaneously.
- A course scheduling automation agent detects conflicts and resolves them institution-wide.
- A student advising agent provides equal-quality support whether the student is on the main campus, a regional campus, or online.
This ensures equity, consistency, and efficiency across the entire university system.
The Role of Standardized Governance Protocols in Scaling Agentic AI
Governance is not optional. It is the foundation of safe, explainable, trusted AI deployment.
As institutions refine these frameworks, many of the same principles now guiding AI in elementary education such as transparency, data protection, and age appropriate autonomy also shape how universities scale agentic AI responsibly across campuses.
Standardized governance protocols:
1. Ensure FERPA-Aligned Data Access
Agentic AI must follow strict rules about:
- What student data can it access?
- How does it store and process that data?
- What decision-making logs must be kept?
It prevents unauthorized access and maintains student trust.
2. Maintain Algorithmic Transparency
Using NIST AI RMF and AI governance in education guidelines, universities build explainability dashboards that reveal:
- Why did an AI make a decision?
- What data influenced the decision?
- Whether bias was detected?
3. Standardize Policies Across Campuses
Agentic AI becomes more effective when rules are unified:
- grading policies
- attendance thresholds
- advising escalation protocols
- Faculty workload rules
- scheduling constraints
4. Define Autonomy Levels
Not all agents need full autonomy. Governance specifies:
- human-in-the-loop
- human-on-the-loop
- fully autonomous actions
5. Protect Academic Integrity
Agentic AI integrates systems for:
- plagiarism detection
- exam integrity
- student identity verification
6. Align With Global AI Ethics Standards
Using frameworks from:
- UNESCO
- OECD
- EDUCAUSE
- Stanford HAI
Note: These guidelines ensure fairness, accountability, and transparency.
How Agentic AI Streamlines Multi-Campus Operations?
1. Academic Administration Automation
Agentic AI eliminates administrative fragmentation by orchestrating complex tasks across campuses.
Tasks include:
- Cross-campus course scheduling automation
- AI-driven enrollment management
- academic catalog updates
- transcript and degree audit automation
- staffing and class assignment
- compliance audits
Example: An autonomous scheduling agent analyzes faculty availability, campus constraints, classroom locations, and student demand to produce a unified multi-campus course schedule, something that previously took weeks of manual coordination.
2. Personalized Student Advising at Scale
Through AI student advising agents, universities can offer:
- 24/7 advising availability
- degree progress monitoring
- real-time alerts for risk factors
- personalized course recommendations
- automatic referrals to advisors
3. Intelligent Teaching & Learning Systems
Agentic AI enhances learning through:
- AI teaching assistants
- AI classroom augmentation tools
- Intelligent tutoring systems
- personalized instruction engines
- adaptive learning systems
Agents track student progress to:
- Adjust content difficulty
- Identify competency gaps
- recommend remediation
- enable mastery-based progression
- Enhance learning outcome optimization
Reminder: This makes learning more student-centered, personalized, and data-driven.
4. LMS Orchestration Across All Campuses
Agentic AI transforms LMS operations by:
- Updating course modules intelligently
- identifying low-engagement weeks
- integrating multimedia content
- ensuring ADA and WCAG compliance
- monitoring academic integrity signals
A single decision by a workflow orchestration AI can update hundreds of course shells in minutes.
5. Compliance, Security & Governance Enforcement
Autonomous governance agents monitor:
- FERPA
- GDPR
- academic integrity
- faculty compliance
- LMS data access
- audit logs
- user authentication
- access privileges
- retention policies
This reduces institutional risk dramatically.
6. Multi-Campus Resource Optimization
Agentic AI coordinates:
- classroom allocation
- Faculty workload balancing
- intercampus shuttle scheduling
- library resource sharing
- lab scheduling
For example:
A science lab in Campus B that is underutilized can be recommended for overflow students from Campus A. AI sees opportunities humans often miss.
Real-World Case Studies
Case Study 1: Arizona State University — Autonomous Student Service Agents
ASU implemented AI-powered autonomous agents across advising, enrollment, and student support.
Results:
- 30% reduction in response times
- Increased advising access for 120,000+ students
- Seamless multi-campus policy unification
Case Study 2: Georgia State University — Predictive Success AI
GSU uses predictive agents that analyze 800+ data points per student.
Outcomes:
- 20% increase in retention
- 10% faster graduation rates
- Major impact across multiple campuses and online divisions
Case Study 3: University of Michigan — Multi-Agent Research & Compliance Operations
UMich deploys multi-agent systems for:
- grant administration
- research compliance
- cross-departmental audit protocols
They achieved a 25% faster processing time for federal research grants.
AI Orchestration Across Multi-Campus Functions
| Function | Agentic AI Role | Governance Protocol | Benefit |
| Scheduling | Autonomous scheduling agent | Standardized academic policy | System-wide consistency |
| Advising | Predictive student advising agent | FERPA, NIST | Personalized equal support |
| Enrollment | Demand forecasting agent | Policy alignment | Optimized class sizes |
| LMS | Learning orchestration agent | ADA, academic integrity | Adaptive, equitable learning |
| Compliance | Autonomous audit agent | GDPR, UNESCO | Continuous institutional compliance |
Ethics, Risks & Mitigation
Risk 1: Over-Autonomy
Mitigation: Human-in-the-loop supervision.
Risk 2: Data Privacy
Mitigation: FERPA-aligned access controls.
Risk 3: Academic Integrity
Mitigation: AI-enhanced detection systems.
Risk 4: Algorithmic Bias
Mitigation: bias detection systems + diverse datasets.
Risk 5: Governance Drift
Mitigation: annual model audits + version control.
Future of Agentic AI: The Next Decade in Higher Ed
Over the next 10 years, universities will evolve into AI-augmented ecosystems, where:
- Agentic AI performs 50% reduction in time and effort
- Intelligent tutoring systems deliver personalized learning
- digital identity models track lifelong learning progress
- AI curriculum frameworks dynamically adjust learning pathways
- Multi-agent orchestration handles campus-wide operations
The institutions implementing ethical, transparent governance protocols now will define the future of global education.
Conclusion
The future of higher education belongs to institutions capable of orchestrating complexity with intelligence, safety, and consistency.
Agentic AI in higher education, when paired with strong, standardized governance protocols, creates a unified academic infrastructure that scales across campuses, enhances equity, improves student outcomes, strengthens academic integrity, and drives digital transformation responsibly.
Universities implementing these frameworks today become tomorrow’s global leaders, resilient, future-ready, and academically superior.
If your institution wants to deploy agentic AI across campuses with full FERPA, GDPR, UNESCO, and EDUCAUSE compliance.
The team at kogents.ai can assist you in designing, building, and implementing end-to-end AI governance frameworks and autonomous university agent ecosystems that unlock scalable, ethical transformation.
FAQs
What is agentic AI in higher education?
It refers to autonomous AI agents that make independent decisions, perform actions, and support academic and administrative functions across multiple campuses.
How do agentic AI systems differ from generative AI?
Generative AI creates content; agentic AI acts, reasons, and executes complex workflows at scale.
How do AI agents ensure compliance across campuses?
Through FERPA, GDPR, NIST, and UNESCO, governance rules are built into each agent’s decision layer.
What are examples of agentic AI used in teaching?
AI teaching assistants, personalized learning agents, adaptive learning systems, and intelligent tutoring systems.
How does agentic AI improve student success?
Agents predict risks, recommend courses, adjust learning pathways, and provide 24/7 personalized advising.
What are the key risks of multi-campus AI deployment?
Bias, data privacy violations, over-autonomy, compliance drift, and inconsistent decision-making.
Which universities currently use agentic AI?
ASU, GSU, UMich, MIT, and institutions participating in Stanford HAI and EDUCAUSE programs.
Is agentic AI safe for academic integrity?
Yes — when combined with integrity monitoring, explainability tools, and ethical governance.
How does agentic AI reduce operational costs?
Through automation of scheduling, advising, enrollment, compliance, and LMS orchestration.
Can agentic AI replace educators?
No, it augments instruction, enabling faculty to focus on coaching, creativity, and mentorship.