If you’re a solopreneur wearing every hat, marketer, salesperson, customer-service rep, creator, and analyst, you’ve probably asked yourself: Should I hire a virtual assistant or use an AI agent?
In 2025, that question defines the next era of one-person entrepreneurship. The distinction between AI agents vs virtual assistants isn’t trivial.
It’s the difference between a tool that waits for your command and a digital team member that takes initiative.
For solopreneurs, choosing correctly can mean freeing 40 hours a month and doubling output without hiring. This blog will help you decide.
Key Takeaways
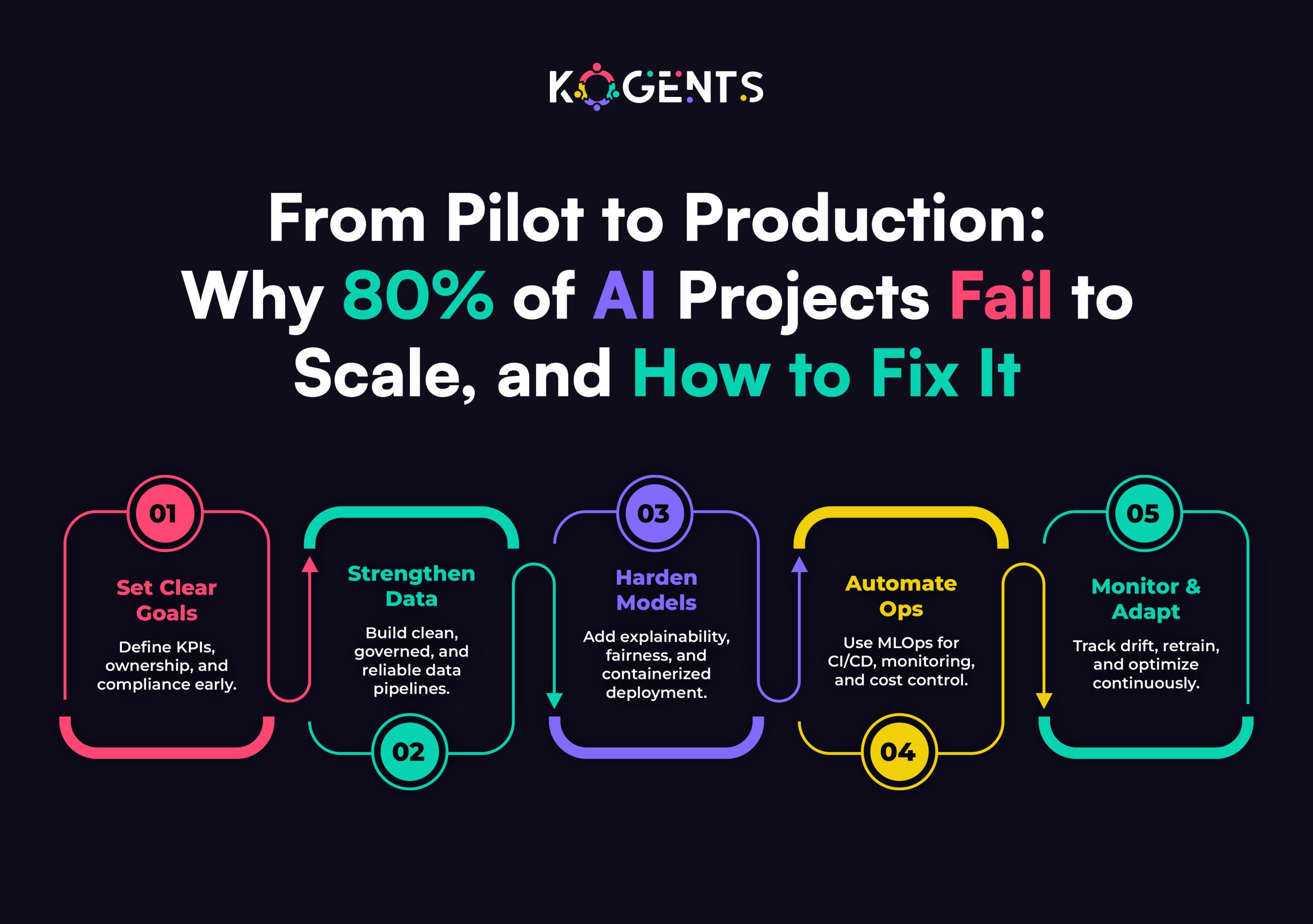
- Autonomy is the dividing line: virtual assistants are reactive; AI agents act independently toward a goal.
- Solopreneur fit depends on workflow: simple repetitive tasks → virtual assistant; multi-step strategic tasks → AI agent.
- Cost vs Leverage: assistants are cheaper and quicker to deploy, agents provide greater scalability and ROI.
- Hybrid models win: start with a virtual assistant, then for complex tasks, automate with AI agents.
- Future advantage: early adoption of agentic AI helps solopreneurs scale like micro-enterprises.
What Are Virtual Assistants?: The Reactive Helpers
A virtual assistant (VA) is a user-initiated, conversational agent that performs tasks when prompted, schedules a meeting, drafts an email, and summarizes a document.
They rely on natural-language processing (NLP) and human-computer interaction (HCI) principles to interpret your request and act.
- Typical traits: reactive, single-step, predictable.
- Examples: Google Assistant, Siri, or business tools like ChatGPT for drafting or scheduling.
- Best for: simple automation, quick replies, and routine tasks.
AI Agents: The Autonomous Operators
- Traits: proactive, multi-step workflow automation, contextual decision-making.
- Powered by: large language models (LLMs), machine learning (ML), and multi-agent systems.
- Best for: lead generation, content pipelines, business process automation (BPA), and decision-support tasks.
Why Solopreneurs Care about AI Agents in 2025?
As a solopreneur, you wear many hats: marketer, seller, service-deliverer, admin, and customer support. Your time is finite; your resources are constrained.
According to one Medium piece:
| Key priorities: scale without hiring, reduce time on repetitive tasks, keep quality and personal touch, stay agile and lean. |
Deep Dive: AI Agents vs Virtual Assistants
Here’s a detailed comparison tailored for solopreneurs:
| Feature | Virtual Assistant | AI Agent |
| Initiation method | User initiates (you say “Draft blog post”) | Goal initialized (you say “Generate content strategy for next quarter”) |
| Autonomy level | Low, waits for input | High, can operate, monitor, and act without constant prompts |
| Workflow length | Short (single or few steps) | Multi-step, may span systems, time, tasks |
| Decision complexity | Simple decisions (yes/no, choose an option) | Complex decision-making (prioritise leads, select content topics, trigger campaigns) |
| Learning/adaptation | Modest, improves via rules/customisation | Strong — uses feedback/metrics, adapts over time, may integrate memory |
| Integration with tools | Basic (calendar, email, chat) | Deep (CRM, analytics, APIs, multiple systems) |
| Setup & maintenance cost | Lower, easier onboarding | Higher cost, more setup, requires monitoring |
| Risk & oversight | Lower risk, easier to control | Higher risk if mis-configured, needs governance |
| Best for a solopreneur when … | Need assistance with routine tasks, want quick wins | Need to scale workflows, automate growth processes, and handle complexity |
| ROI-timeframe | Shorter | Longer but potentially larger payoff |
Autonomy, Decision-Making, Integrations
- Virtual assistants are essentially responsive: they wait for your command, then act. They help lighten the load, but you still decide what to ask.
- AI agents are proactive: you establish a goal (e.g., “qualify 500 leads this month”), the agent breaks it down, acts (runs outreach, scores leads, enters CRM), monitors progress, and adjusts.
- For solopreneurs, this means: if your workflow is linear and repeatable (e.g., “post blog → send to email list → schedule social”), a virtual assistant may suffice.
- If your workflow is more complex (e.g., capture leads from multiple channels, score them, nurture, schedule a call, send a tailored proposal), an AI agent offers more value.
When a Virtual Assistant Suffices?
- When your tasks are predictable, repeatable, and low-risk (scheduling, email replies, formatting content).
- When you don’t yet have the budget/time for a complex system set-up.
- When you want to stay simple and maintain direct control.
- When you prefer human-like flexibility and can tolerate more manual input.
When is an AI Agent Preferable?
- When you have growth goals that exceed what one person can manually handle.
- When you need to orchestrate workflows across systems (CRM, email, calendar, analytics).
- When you want tasks completed autonomously, then AI agents’ benefits can’t be overlooked.
- When you’re looking for scalability and time leverage.
- When you can invest in setup, governance, and ongoing monitoring (to avoid “agent misbehaviour”, data issues, etc.).

Use-Cases and Case Studies for Solopreneurs
Case Study 1: Content Creation & Scheduling
Context: A freelance writer/solo content marketer needs to produce four blogs/month, repurpose them into eight social posts, send a weekly newsletter, and engage with comments.
Virtual Assistant Approach: Use a conversational assistant (e.g., GPT-4 via chat) for drafting blog posts, schedule posts manually through a social-media scheduler, and send newsletters via email software.
Outcome: Time spent is still significant; still lots of manual input.
AI Agent Approach:
Deploy an AI agent that:
- (a) monitors trending topics in a niche,
- (b) draft blog outline and first draft,
- (c) formats into social posts,
- (d) schedules posts in the calendar,
- (e) monitors engagement metrics and loops feedback into the next batch.
Outcome: Content pipeline becomes semi-autonomous, the solopreneur spends time refining, not producing from scratch.
Case Study 2: Lead Qualification & Outreach Automation
Context: A consultant running a solo business wants to convert leads from website form, LinkedIn, and email; needs to qualify, score, and schedule discovery calls.
Virtual Assistant Approach: A virtual assistant tool handles form responses, sends templated replies, and alerts the consultant to manual follow-up. Some manual scoring required.
AI Agent Approach: An AI agent monitors lead sources in real time, enriches each lead with public data (LinkedIn, company info), scores leads with an ML model, sends personalised outreach email, sets up a meeting if criteria are met, updates CRM, and escalates to a human if the lead meets “hot” threshold.
Outcome: The solopreneur wakes up to a list of qualified leads with meeting slots scheduled; less manual sorting and chasing.
Result: Lead conversion increases (e.g., conversion rate 15–20% instead of 5–7%). Time freed to focus on closing, not sorting.
This mirrors the AlphaGamma example:
“Automated lead lists … value-first outreach converting at 15–20% … majority of time spent on strategic work.”
Future Trends: Looking Ahead!
- Multi-agent systems (teams of agents interacting) will mature.
- MoveWorks identifies this as an evolution from single agents.
- Cost barriers continue to drop; more platforms are offering no-code or low-code agent creation for solo businesses.
- Example: “Most solopreneurs are building AI agents completely backwards,” suggests that accessible frameworks now exist.
- Increased autonomy but also increased need for oversight and governance (ethical AI, data privacy, safety).
- For solopreneurs: early adopters of agentic automation will gain an advantage; those sticking with manual or reactive tools risk falling behind.
Conclusion
In the debate of AI Agents vs Virtual Assistants, it’s not about which is better, but which aligns with your stage and goals.
Virtual assistants boost efficiency for routine tasks, while AI agents scale workflows and revenue through autonomy.
The smart solopreneur blends both, starting small, automating one workflow, then evolving into a micro “AI-powered team.” Success depends on clear goals, good processes, and iterative refinement.
Ready to build your next-generation solo system? Visit the best agentic AI company in town, named Kogents.ai, and turn automation into acceleration.
FAQs
How do AI agents work compared to virtual assistants?”
Virtual assistants typically rely on conversational AI or natural-language processing (NLP) to interpret user commands and execute simple tasks. AI agents go further: they decompose goals into subtasks, integrate tools/APIs, monitor context, and adapt decisions over time.
Are AI agents smarter than virtual assistants?”
“Smarter” depends on context. AI agents are more capable in workflows that require decision-making, tool integrations, and autonomy. Virtual assistants may suffice (and be smarter from a cost/time perspective) for simpler tasks. Intelligence here is functional rather than intrinsic.
What makes an AI agent autonomous vs a virtual assistant reactive?
Autonomy means the system can act without constant human prompts, monitor progress, and choose actions. Reactivity means the system responds when asked. The difference lies in goal-orientation and initiative.
Which is better for my business: a virtual assistant or an I agent?
It depends on your business needs, workflow complexity, budget, and growth targets. For many solopreneurs, starting with a virtual assistant makes sense. If you have scalable workflows and want to amplify output, an AI agent is better, or a hybrid strategy. Refer to the decision framework above.
Can a solopreneur without technical skills use AI agents?
Yes, many no-code or low-code platforms now offer AI-agent builders tailored for small businesses. The key is to pick a manageable workflow, follow best practices (goal definition, monitoring, feedback loops). Solopreneurs don’t need to build from scratch.
Will virtual assistants become obsolete because AI agents will replace them?
Unlikely in the near term. Virtual assistants serve many simpler tasks efficiently and low cost. AI agents scale complexity. For many solo businesses, a hybrid model (virtual assistant for certain tasks, agent for others) makes sense. They complement each other rather than one replacing the other entirely.