Visualize a scenario: A potential customer lands on your website at 11 PM, ready to buy.
They have questions.
They need reassurance.
But there’s no one to answer.
By morning, they switch to your competitor’s website.
This scenario results in millions of dollars in lost revenue every single day.
In today’s hyper-connected marketplace, where customer experience defines competitive advantage, the gap between customer inquiry and business response has become the silent revenue killer.
According to HubSpot Research, 82% of consumers expect an immediate response to sales questions, yet most businesses still operate on legacy customer service models that can’t keep pace.
But chat automation for higher conversions, not just another marketing buzzword, but a fundamental shift in how modern businesses capture, nurture, and convert leads in real-time.
Whether you’re a SaaS founder watching qualified leads slip through the cracks, an ecommerce manager struggling with cart abandonment, or a marketing director pressured to prove ROI, automated conversational marketing represents your path to measurable revenue growth.
Companies implementing conversion-focused chat automation identify conversion rate increases.
They’re capturing leads while competitors sleep, nurturing relationships across multiple touchpoints, and building automated customer journeys that feel remarkably human.
In this guide, we’ll dissect exactly how conversational AI automation works across the three platforms that matter most: WhatsApp, Instagram, and your website.
You’ll discover proven frameworks, real-world implementations, and actionable strategies to transform conversations into revenue.

Navigating Chat Automation for Higher Conversions
Chat automation isn’t about replacing human connection; it’s about amplifying it.
Modern conversational AI systems combine Natural Language Processing (NLP), Machine Learning, and sophisticated intent recognition to understand context, anticipate needs, and guide conversations toward conversion.
The Core Components of Effective Chat Automation
-
Intent Detection: Understanding what customers actually want, not just what they say. Advanced NLP interprets context, emotion, and urgency.
-
Dynamic Conversation Flows: Adaptive pathways that respond to user behavior in real-time, not rigid decision trees.
-
Omnichannel Synchronization: Seamless context retention across WhatsApp, Instagram, website, and email touchpoints.
-
Intelligent Lead Qualification: Automated scoring based on engagement patterns, questions asked, and behavioral signals.
-
CRM Integration: Automatic data capture, enrichment, and routing to sales teams with full conversation context.
WhatsApp Chat Automation: Turning Private Conversations into Revenue
WhatsApp boasts 2+ billion active users and unparalleled engagement rates. Unlike email’s 20% open rates, WhatsApp messages achieve open rates with 90% read within 3 minutes.
This platform excels for high-touch customer relationships requiring trust and immediacy.
Strategic WhatsApp Automation Use Cases
-
Abandoned Cart Recovery: Businesses rely on AI agents for abandoned cart recovery to re-engage buyers and reclaim lost revenue.
-
Appointment Scheduling: Automated booking, confirmations, and reminders reduce no-shows by 45-60%.
-
Customer Support: Instant resolution of common queries, order tracking, and FAQ responses with human escalation for complex issues.
-
Post-Purchase Engagement: Onboarding sequences, usage tips, upsell opportunities, and review requests.
-
Lead Nurturing Campaigns: Drip campaigns with rich media delivering educational content that guides prospects toward purchase decisions.
WhatsApp Business API Implementation Framework
The WhatsApp Business API enables sophisticated automation while maintaining platform compliance. Key considerations:
-
Template Message Approval: Pre-approved message templates for outbound communications ensure compliance while enabling scale.
-
24-Hour Session Window: Free-form conversations permitted within 24 hours of customer-initiated contact; template messages required afterward.
-
Rich Media Integration: Images, videos, documents, and interactive buttons enhance engagement and conversion.
-
Quality Rating Monitoring: Maintain high quality ratings by balancing automation with value to avoid being flagged as spam.
Instagram Direct Message Automation: Visual-First Conversion
Instagram DM automation leverages the platform’s visual nature for product discovery and impulse purchases.
With 69% of shopping enthusiasts turning to Instagram for product discovery, automation here captures high-intent buyers at the peak of interest.
High-Converting Instagram Automation Strategies
-
Story Reply Automation: Capture product interest from story interactions, automatically sending product details, pricing, and purchase links.
-
Comment-to-DM Funnels: Users commenting specific keywords trigger automated DMs with personalized offers.
-
Lead Magnet Distribution: Automated delivery of guides, discounts, or exclusive content in exchange for engagement.
-
Product Recommendation Engines: AI-powered suggestions based on browsing behavior, past interactions, and stated preferences.
-
Influencer Partnership Automation: Scaling influencer campaigns with automated response systems handling inquiries generated by creator content.
Website Chat Automation: The Controlled Conversion Environment
Your website represents your most controlled conversion environment.
Website chat automation captures visitors at peak interest, qualifies intent, and routes appropriately, all while gathering zero-party data for enhanced personalization.
Advanced Website Chat Automation Tactics
-
Behavioral Triggering: Launch chat based on exit intent, time on page, scroll depth, or specific page visits.
-
Dynamic Content Personalization: Adapt conversation flows based on referral source, UTM parameters, or browsing history.
-
Progressive Profiling: Gather information incrementally across multiple interactions rather than demanding forms upfront.
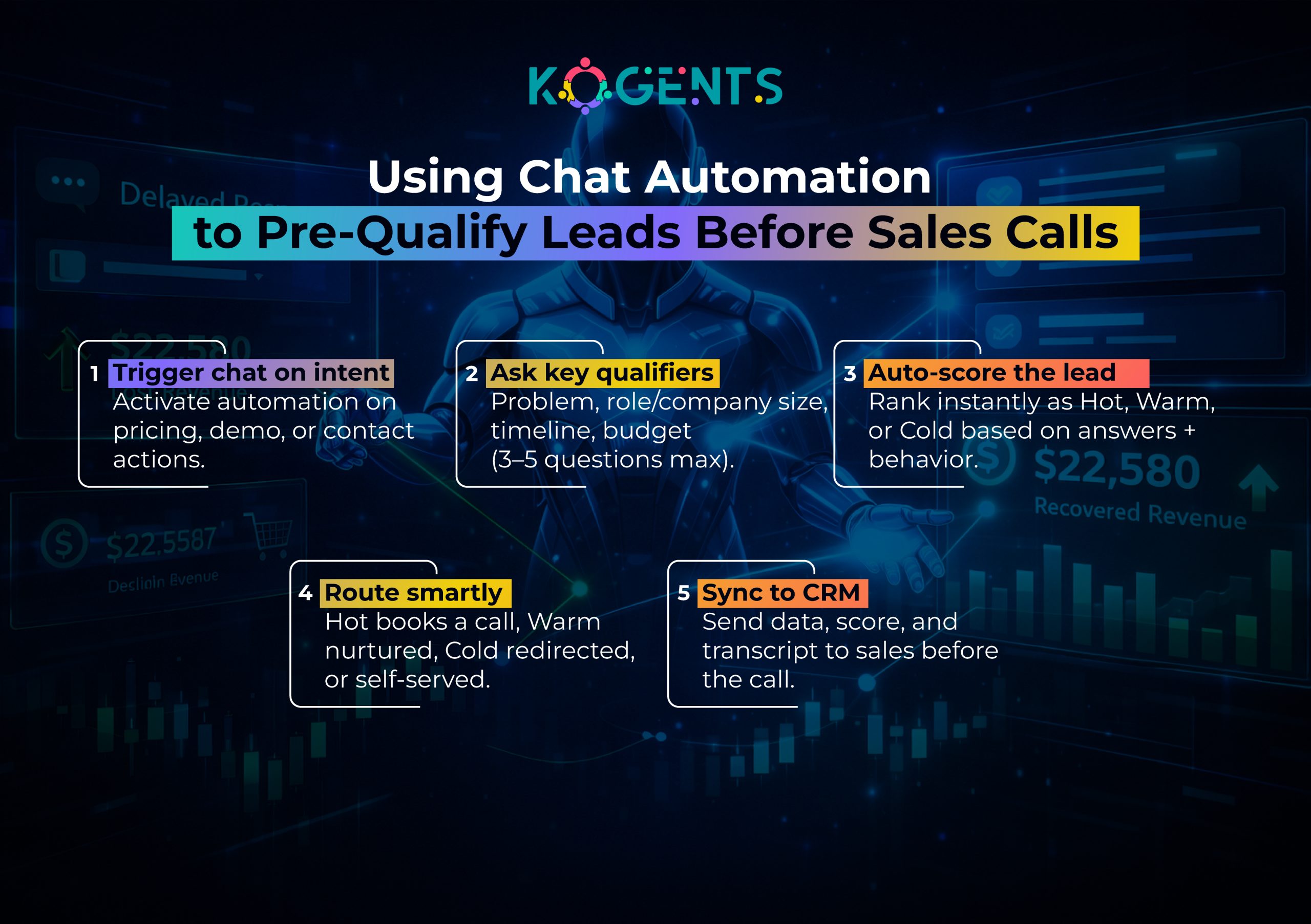
-
Real-Time Lead Scoring: Assign qualification scores dynamically as conversations unfold, prioritizing hot leads for immediate sales engagement.
-
Meeting Scheduling Integration: Qualified prospects book directly with sales reps through integrated calendar systems.
Platform Comparison: Where to Prioritize Your Automation
Each platform offers distinct advantages. Strategic implementation requires understanding where your audience concentrates and which platform aligns with your conversion objectives.
|
|
|
Website |
Best For: High-touch relationships, appointment bookings, customer support |
Best For: Visual products, impulse purchases, brand engagement. |
Best For: Lead qualification, complex sales, demo requests. |
98% open rate, 90% read in 3 minutes |
70% of shoppers use it for product discovery. |
Complete behavioral tracking & context. |
Challenge: Template approval requirements, 24-hour windows |
Challenge: Limited to Meta-approved partners, visual dependency. |
Challenge: Requires traffic generation, technical integration. |
Chat Automation Network: How WhatsApp, Instagram & Website Work Together
Think system, not channels.
- Instagram → Ignites demand (stories, comments, discovery)
- Website → Captures intent (pricing, demos, high-intent actions)
- WhatsApp → Closes & retains (trust, follow-ups, conversions)
Unravel How the Automation Network Works
Multiple entry points: Users start conversations on Instagram, the website, or WhatsApp.
One shared intelligence layer: All interactions feed into a single AI brain that tracks intent, behavior, and lead score across platforms.
Smart cross-channel routing: Discovery moves to conversion automatically (Instagram → WhatsApp, Website → WhatsApp, WhatsApp → checkout or booking).
Conversion actions triggered: Book calls, recover carts, schedule appointments, or escalate to sales, based on lead quality.
Continuous optimization loop: Every conversation improves scoring, messaging, and conversion paths.
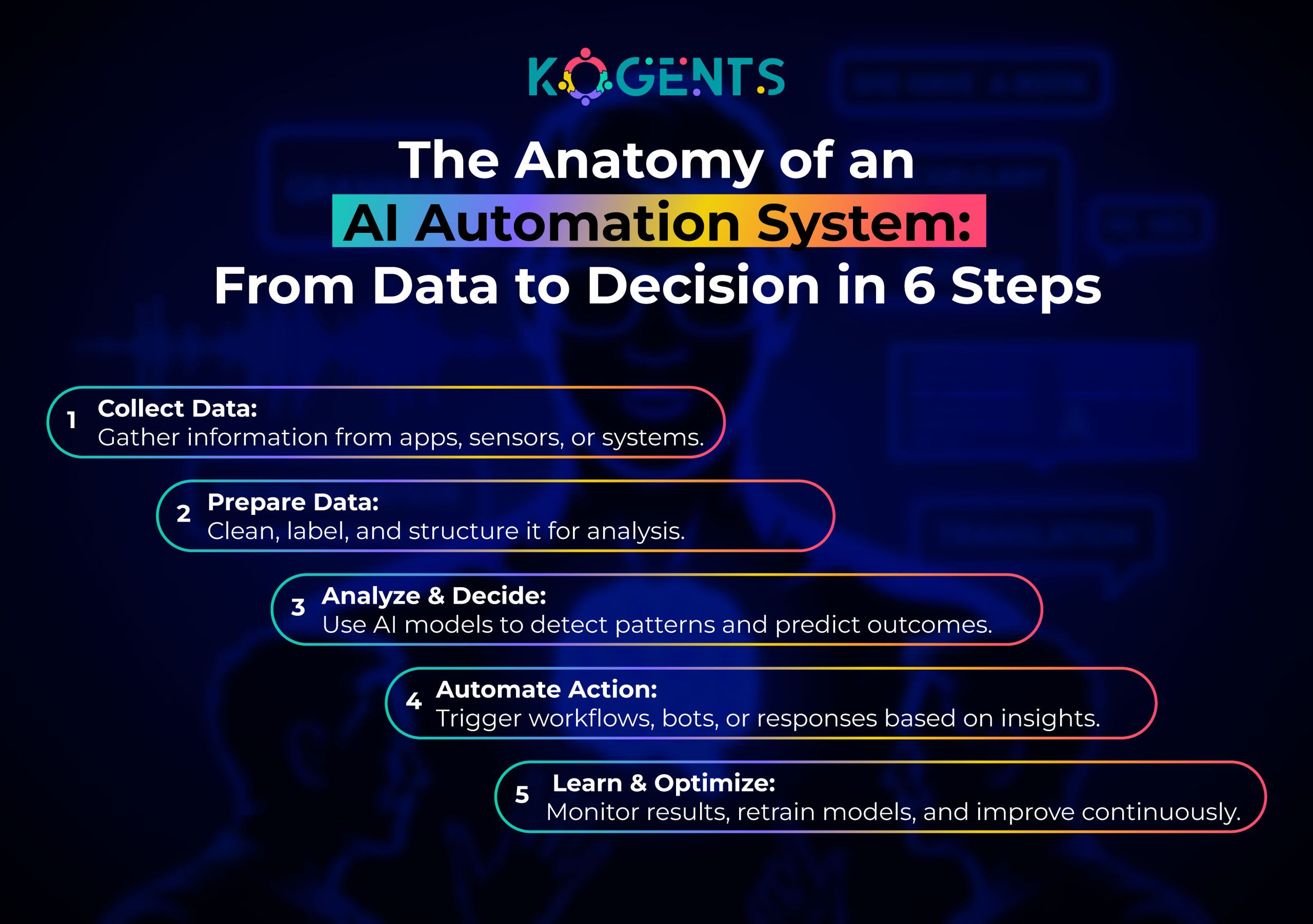
The 5-Phase Chat Automation Implementation Framework
Phase 1: Conversion Intelligence Audit
Before building automation, understand where conversations currently fail:
-
Analyze support tickets, identifying repetitive questions.
-
Review sales call recordings for common objections and questions.
-
Map customer journey, identifying friction points where prospects drop off.
-
Survey customers about preferred communication channels and timing.
Phase 2: Platform Selection & Prioritization
Don’t launch everywhere simultaneously. Prioritize based on:
-
Audience concentration: Where do your highest-intent customers spend time?
-
Use case alignment: Match platform strengths to your primary conversion goals.
-
Implementation complexity: Start simple with the highest-ROI opportunities.
Phase 3: Conversation Design & Testing
Effective automation requires exceptional conversation design:
-
Write conversationally, not corporately. Mirror how customers actually speak.
-
Build branching logic handling edge cases without frustrating users.
-
Establish clear escalation paths to human agents when needed.
-
A/B test conversation flows continuously, optimizing for conversion.
Phase 4: Integration & Deployment
Technical excellence determines automation success:
-
Integrate with CRM for seamless data flow and lead routing.
-
Connect calendar systems for automated appointment scheduling.
-
Implement analytics tracking conversation-to-conversion attribution.
-
Deploy gradually, testing with small traffic percentages before scaling.
Phase 5: Optimization & Scaling
Launch is just the beginning. Continuous improvement drives results:
-
Review conversation transcripts weekly, identifying improvement opportunities.
-
Track KPIs: conversation rate, completion rate, conversion rate, CSAT scores.
-
Expand to additional platforms as you prove ROI on initial implementation.
-
Refine the machine learning mode; LS continuously improves intent recognition.
Real-World Applications: Chat Automation Success Stories
Case Study 1: SaaS Company — 312% Increase in MQLs
Challenge: Mid-market SaaS company struggled with low demo request conversion despite high traffic.
Solution: Implemented website chat automation with behavioral triggers targeting pricing page visitors spending 60+ seconds.
Results: 312% increase in marketing qualified leads, 45% reduction in cost per acquisition, 60% of demos now booked through automated chat.
Case Study 2: E-commerce Brand — $2.3M Recovered Revenue
Challenge: Fashion retailer is losing revenue due to a 73% cart abandonment rate.
Solution: WhatsApp abandoned cart automation with personalized product images and one-click checkout.
Results: $2.3M in recovered revenue over 6 months, 32% cart recovery rate, 4.2x ROI on automation investment.
Case Study 3: Healthcare Provider — 91% Appointment Fill Rate
Challenge: Dental practice facing a 35% no-show rate, costing thousands monthly in lost revenue.
Solution: WhatsApp appointment automation, including booking, confirmations, reminders, and easy rescheduling.
Results: 91% appointment fill rate (up from 65%), 200+ hours annually saved in administrative work, 28% increase in patient satisfaction scores.
Key Insight: The highest-performing chat automation implementations share one trait: they solve specific, measurable problems rather than attempting to automate everything at once.
Your Competitive Advantage Awaits!
Chat automation for higher conversions isn’t futuristic or nice-to-have.
It’s the operational backbone separating companies capturing market share from those watching opportunities slip away.
Every unanswered question, every delayed response, every frustrated customer represents revenue you’ve earned through marketing but failed to capture through execution.
WhatsApp’s privacy, Instagram’s visual engagement, and your website’s controlled environment each offer unique conversion advantages.
The businesses winning aren’t choosing one platform; they’re orchestrating seamless omnichannel chat automation that meets customers wherever they are, remembers context across touchpoints, and guides them toward outcomes serving both customer needs and business objectives.
The implementation journey requires strategic thinking, technical competence, creative excellence, and analytical rigor.
The competitive moat being built right now isn’t technology; these platforms are available to everyone.
It’s the operational excellence, conversational AI automation, and customer understanding you develop through deliberate implementation and continuous improvement.
Transform Conversations Into Revenue with Kogents!
While chat automation delivers impressive results, Kogents.ai, being the best agentic AI company, takes conversational intelligence to an entirely different level, with autonomous systems that don’t just respond to queries but proactively solve problems, make decisions, and orchestrate complex workflows across your business ecosystem.
Why Kogents Excels:
-
Autonomous decision-making systems that analyze context, evaluate solutions, and execute optimal actions without human intervention.
-
Cross-system intelligence actively managing CRM, marketing automation, and calendars like orchestral conductors.
-
Continuous learning architecture that refines intent detection and personalization in real-time.
-
Industry-specific vertical AI pre-trained on your sector’s challenges, terminology, and workflows.






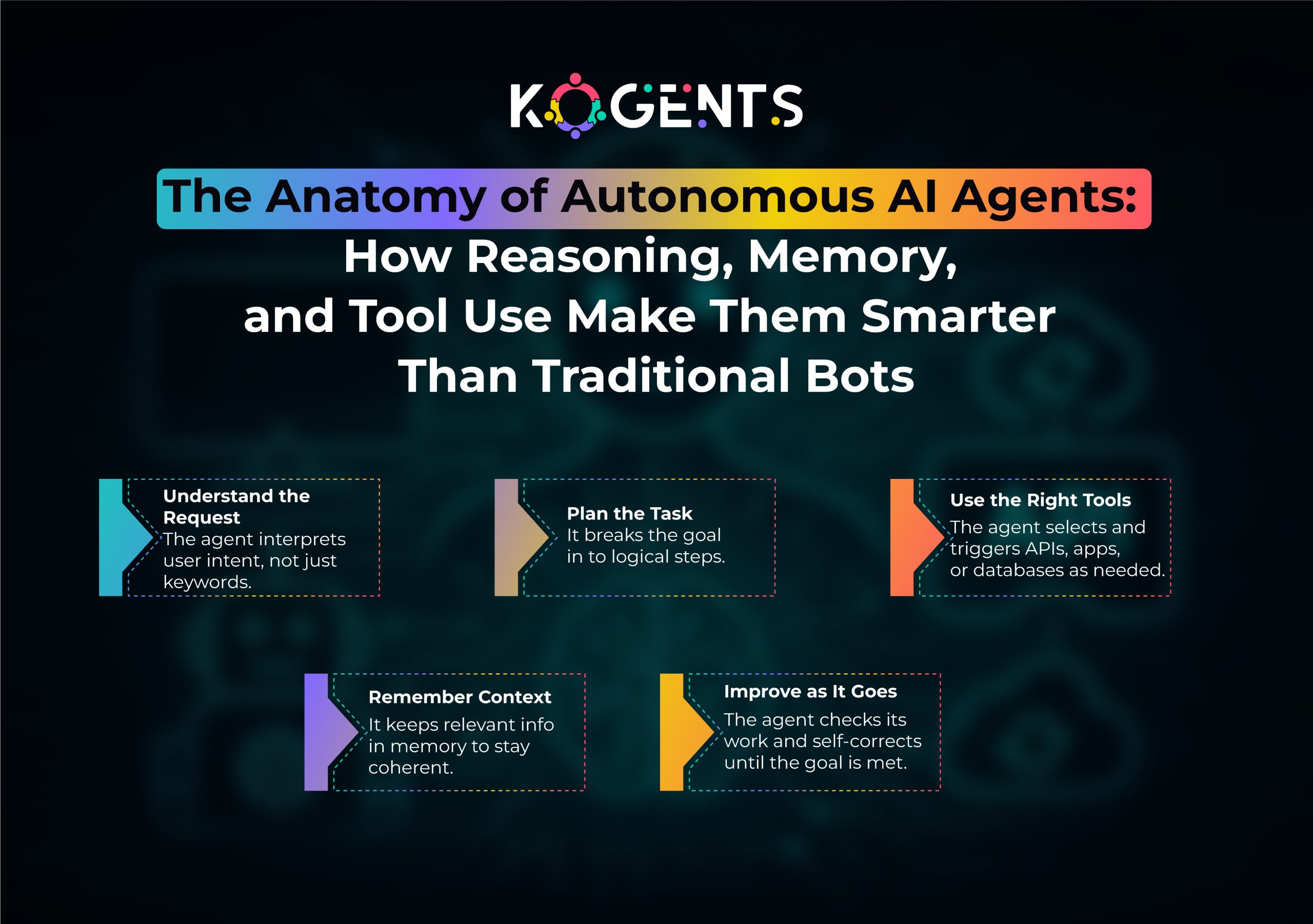

 AI Agents vs Workflows — The Core Differences
AI Agents vs Workflows — The Core Differences