The healthcare industry is undergoing a profound digital acceleration. Hospitals, clinics, payers, and telemedicine networks are integrating Healthcare AI tools, AI tools for healthcare, AI-powered healthcare systems, and AI healthcare solutions to improve diagnostics, automate workflows, empower clinicians, and enhance patient outcomes.
But with this transformation comes an equally significant surge in cyberattacks targeting PHI, data so valuable that it sells for $250–$1,000 per patient record on underground markets.
To confront this crisis, the world’s most advanced healthcare systems, from the NHS to Mayo Clinic, Cleveland Clinic, Mount Sinai, and Stanford Medicine, are adopting a dual approach: AI-driven healthcare intelligence fused with zero-trust security architectures.
This powerful combination ensures that AI can process, analyze, and generate medical insights, while zero-trust ensures that every identity, device, model, connection, and data request is fully verified before any PHI is exposed.
Together, they create the most bulletproof PHI security ecosystem possible.
Key Takeaways
- Zero-trust transforms the Healthcare AI agent from a high-risk implementation into a fully controlled PHI-safe ecosystem.
- AI expands PHI access, but zero-trust closes every attack surface, from EHR endpoints to telemedicine devices.
- Zero-trust cuts breach impact, making it the most effective model for AI-driven healthcare systems.
- AI requires identity-aware, continuously authenticated data streams; zero-trust provides this foundational layer.
- Kogents.ai offers an integrated HIPAA-ready, zero-trust AI platform purpose-built for healthcare workflows.
What Healthcare AI Tools Really Are?
Healthcare with AI is no longer limited to research labs; it is now embedded across patient care, diagnostics, hospital operations, and remote monitoring systems.
Healthcare AI tools, medical AI tools, health AI technologies, and AI software for hospitals include systems such as:
AI-Driven Diagnostics & Decision Support
- Detecting tumors, hemorrhages, fractures, and abnormalities in imaging
- Predicting disease progression
- Assisting radiologists with AI diagnostics tools
Clinical Workflow Automation
- Automating triage
- Scheduling and admission workflows
- Revenue cycle coding
- Prior authorization automation
Telehealth & Virtual Care AI
- Healthcare AI assistant for symptom triage
- Remote monitoring with integrated ML
- Predictive alerts for clinical deterioration
Predictive & Analytical AI
- Sepsis prediction
- Readmission reduction
- Real-time risk scoring
- Forecasting patient volumes
EHR & Data Intelligence
- Augmenting EHR data
- Extracting clinical insights
- Reducing physician burnout through AI documentation tools
The power of these tools lies in their ability to rapidly process Electronic Health Records (EHR), imaging, vitals, genomics, and patient-generated data, but they also increase the number of PHI entry points.
This is exactly why zero-trust becomes indispensable.
The Power of Zero-Trust Security in Healthcare
Zero-trust is an identity-first security model based on a non-negotiable principle:
Trust nothing. Verify everything. Always.
Unlike outdated perimeter security, where internal systems are “trusted,” zero-trust treats every user, device, AI tool, and application request as a potential threat until proven otherwise.
Why Zero-Trust Is Perfect for Healthcare
Healthcare has:
- The most diverse user groups (nurses, specialists, labs, pharmacies, insurers).
- The most fragmented systems (EHR, PACS, LIS, RIS, telemedicine, and monitoring).
- The highest stakes (patient lives & compliance).
Zero-trust applies strict, continuous authentication across:
-
- AI models
- API calls
- Imaging systems
- EHR platforms
- Telehealth apps
- IoT and RPM devices
- Cloud ML workloads
Core Capabilities of Zero-Trust
- Micro-segmentation: Every PHI system is isolated; attackers cannot move laterally.
- Least-privilege access: Users see only the minimum PHI required.
- Continuous identity verification: Even logged-in users are repeatedly re-validated.
- Encrypted data pipelines: PHI is encrypted at rest and in motion, aligning with HIPAA.
- Real-time anomaly detection: Detects suspicious AI outputs, queries, or data behaviors.
Zero-trust is the only framework aligned with HHS, NIST, HIPAA, GDPR, and ISO 62304 guidelines, making it essential for AI-driven healthcare.

Why Healthcare AI + Zero-Trust = The Strongest PHI Defense?
AI Agents for Healthcare Automation and zero-trust form a high-security intelligence ecosystem unmatched by traditional cybersecurity models.
Reason 1 — AI Expands Data Access; Zero-Trust Shrinks Exposure
AI requires:
- Massive EHR ingestion
- Imaging datasets
- Lab records
- Genomics
- Wearables and IoT
Note: Without zero-trust, each of these becomes a gateway for attackers.
Zero-trust ensures:
- Only authenticated identities can send or receive PHI
- AI models are identity-bound
- Data requests are validated in real-time.
- Unverified access is rejected instantly
Reason 2 — Zero-Trust Protects Against AI-Specific Cyberattacks
AI introduces new security risks:
- Model poisoning
- Adversarial attacks
- Prompt injection
- Data manipulation
- Model inversion (extracting PHI from models)
Zero-trust adds:
- Input validation
- Output checking
- Model identity controlsAPI integrity verification
- Continuous behavioral monitoring
Reason 3 — AI + Zero-Trust Stops Insider Threats
- 60%+ of PHI breaches come from insiders (HHS OCR 2024).
- Zero-trust blocks unauthorized access even from internal staff.
Reason 4 — Joint Framework Ensures HIPAA & FDA Compliance
AI must be:
- Auditable
- Traceable
- Explainable
- Secure
Zero-trust enforces:
- Data minimization
- Continuous audit trails
- Model-level logs
- FDA-compliant transparency
Reason 5 — AI Becomes Safer, More Accurate, and More Reliable
Zero-trust enforces the cleanest possible data inputs to models, reducing:
- Bias
- Drift
- Noise
- Data leakage risks
This significantly improves the diagnostic accuracy of:
- Imaging AI
- Predictive models
- Clinical AI decision support
Threat Landscape: Why PHI Needs AI + Zero-Trust
Verified Statistics
Healthcare is the #1 cyber target, which is why AI + zero-trust must become standard.
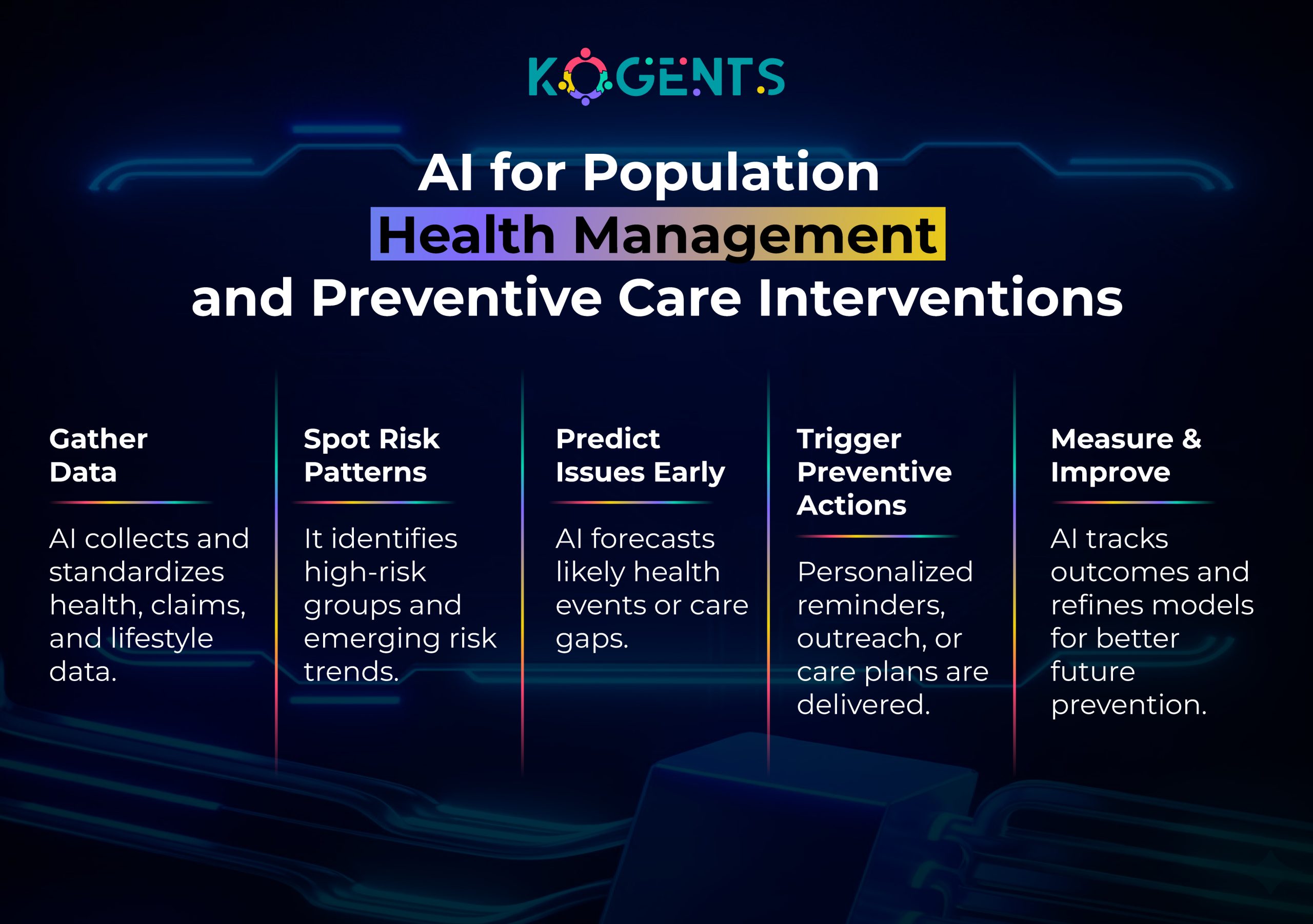
Use Cases Where AI + Zero-Trust Transform PHI Protection
AI Imaging + Zero-Trust
- AI models can only access validated imaging data
- No model can run without identity validation.
- Radiology access logs are fully tracked.
Remote Patient Monitoring AI (RPM)
Zero-trust prevents:
- Device spoofing
- Data manipulation
- Unauthorized signal injection
AI-Assisted Telemedicine
Zero-trust prevents:
- Deepfake patient impersonation
- Unauthorized session access
- PHI screen scraping
Predictive AI for Risk Scoring
Zero-trust ensures:
- Authentic data sources
- Verified model access
- Accurate clinical predictions
Case Studies
Case Study 1: NHS – Predictive AI + Privileged Identity Management
NHS Digital implemented AI for risk scoring backed by zero-trust identity.
Results:
- 71% reduction in unauthorized access
- Stopped the major ransomware spread
Case Study 3: Cleveland Clinic – RPM AI + Zero-Trust Device Access
Cleveland Clinic built a zero-trust infrastructure around its remote monitoring AI.
Results:
- 32% fewer readmissions
- 98% reduction in unauthorized device connections
Comparison Table & Analysis
| Feature | Traditional Security | AI + Zero-Trust PHI Security |
| Access Model | Trust once | Continuous verification |
| Insider Risk | High | Very low |
| PHI Segmentation | Minimal | Full micro-segmentation |
| AI Model Security | None | Model authentication, input validation |
| Audit Trails | Manual & incomplete | Automated HIPAA/FDA-ready |
| Attack Surface | Large | Minimized & identity-bound |
| Clinical AI Reliability | Risky | High fidelity & safe |
Analysis
- Traditional systems focus on perimeter firewalls.
- Zero-trust dismantles this approach by binding every identity, AI model, and data flow to continuous authentication, making it nearly impossible for attackers to move laterally or infiltrate AI workflows.
Challenges
1. Legacy Infrastructure
Most hospitals still run outdated systems incompatible with AI or zero-trust frameworks.
2. Identity Complexity
Healthcare has diverse user roles, making identity orchestration difficult.
3. Vendor Fragmentation
Multiple systems (EHR, PACS, RPM, LIS) require unified zero-trust integration.
4. AI Model Risks
AI suffers from drift, bias, and input manipulation without strict verification.
Implementation Road Map
1. Begin With Identity Modernization
Deploy multi-factor identity, identity governance, and least-privilege access.
2. Add AI Access Segmentation
Micro-segment EHR, imaging, RPM, and AI processing zones.
3. Implement Continuous Monitoring
Track AI model requests, outputs, and anomalies 24/7.
4. Unified Platform Approach
Platforms like Kogents.ai simplify implementation through pre-built zero-trust AI modules.

Conclusion
Healthcare AI tools are reshaping diagnostics, telehealth, risk scoring, EHR intelligence, and remote care. But this innovation also expands access surfaces and increases PHI vulnerabilities.
The only way to maintain accuracy, integrity, and compliance is through a zero-trust security model that verifies every identity, every application, every model, and every connection.
In an era where cyberattacks target healthcare more aggressively than any other industry, the combination of AI intelligence + zero-trust enforcement is not just beneficial, it is essential.
Healthcare leaders who adopt this dual strategy will build the safest, most compliant, and most efficient digital health ecosystems of the future.
Ready to deploy HIPAA-compliant, zero-trust-enforced, enterprise-grade AI across your healthcare workflows?
Book a demo with Kogents.ai and transform your clinical, operational, and telehealth systems with secure, scalable, and regulatory-ready AI.
FAQs
What are Healthcare AI Tools and how do they manage PHI securely?
They analyze, predict, automate, and enhance clinical workflows. When paired with zero-trust, every PHI request is authenticated and logged.
Are AI tools for medical diagnosis HIPAA-compliant?
Yes—if they operate within encrypted, identity-bound, zero-trust environments.
How is AI used in hospitals?
For imaging, triage, documentation, risk scoring, EHR insights, and patient monitoring.
What’s the safest way to deploy AI software for hospitals_?
Zero-trust identity, micro-segmented PHI zones, and continuous AI monitoring.
Can telemedicine AI be exploited?
Yes, but zero-trust prevents impersonation, session hijacking, and device spoofing.
What is the benefit of AI healthcare platforms over traditional software?
They provide predictive intelligence, automation, and clinical decision support.
How do predictive analytics AI tools in healthcare reduce risk?
They forecast deterioration early—preventing sepsis, cardiac events, and readmissions.
Why is zero-trust crucial for clinical AI models?
It protects against poisoning, inversion, manipulation, and identity misuse.
What’s the biggest risk of not using zero-trust with AI?
Unverified access can lead to massive PHI exposure and inaccurate AI outcomes.
Why do hospitals prefer HIPAA-compliant AI tools for healthcare?
They reduce liability, accelerate audits, and maintain patient trust at scale.













 Future Trends in AI Teaching Assistants (2025–2030)
Future Trends in AI Teaching Assistants (2025–2030)