One popular opinion is that most of the teams don’t blow their AI budget on models. Rather, they believe in blowing it on architecture.
Across 2024–2025, enterprises rushed to bolt large language models (LLMs) into everything. POCs looked great.
Demos were magical. But 6–12 months later, many of those systems hit the same wall:
- Pipelines became fragile and unmaintainable
- Cloud model inference costs kept climbing
- Compliance and traceability were an afterthought
- “Quick wins” turned into engineering debt.
The root cause usually wasn’t model quality. It was a conceptual mistake: Treating models like agents.
Static predictive models were used where autonomous AI systems were required.
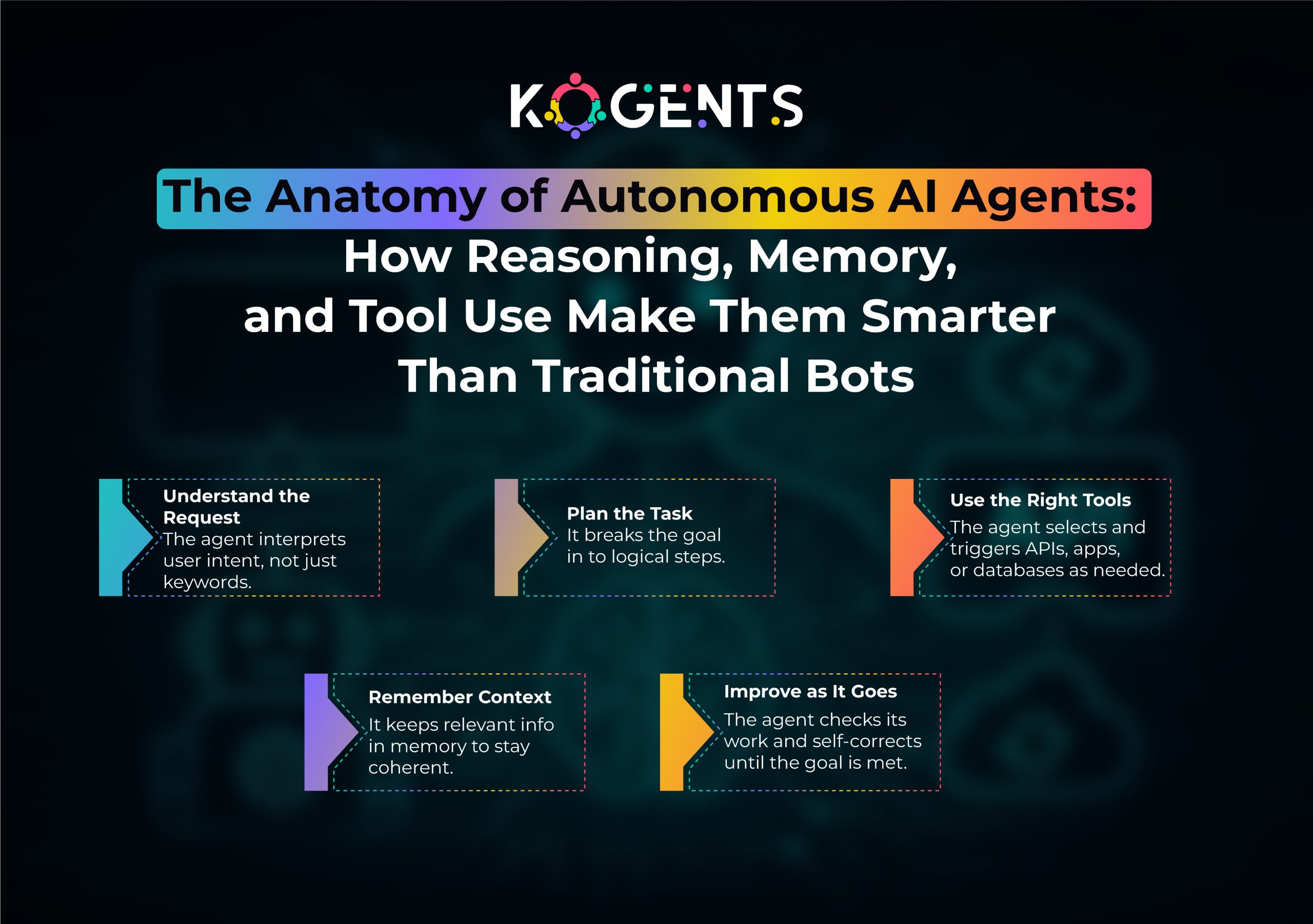
Teams tried to force LLMs to plan tasks, call tools, remember context, and complete workflows, functions that belong to agents, not bare models.
In this article, we’ll unpack the real difference between AI agents vs AI models, show how the wrong choice snowballs into engineering debt, and walk through concrete, research-backed patterns for getting agent-based AI architecture vs model-based AI right, from day one.
Key Takeaways
- The core difference between AI agents and models is that models do pattern recognition, while agents run decision-making algorithms over time using tools, memory, and feedback.
- A purely model-centric AI vs agentic AI approach in automation-heavy use cases leads to fragile glue code, skyrocketing inference costs, and significant long-term engineering debt.
- Notably, Automate with AI Agents, built on top of foundation models, combines LLM-based reasoning, tools, memory, and perception–action cycles into cohesive cognitive architectures.
Why the “AI Agents vs AI Models” Distinction Suddenly Matters?
That’s the pivot:
- First wave: “Can a transformer model or foundation model generate good outputs?”
- Next wave: “Can a multi-agent collaboration of systems plan & execute work with minimal oversight?”
If you keep architecting everything as a simple model inference pipeline when your business needs autonomous decision pipelines, you’re locking in technical debt:
- You over-optimize prompts instead of reasoning engines
- You build rigid DAGs instead of agentic loop–driven workflows
- You keep humans as orchestrators instead of deploying tool-using agents
The stakes are no longer academic; they’re economic and structural.
Architecture: Agent-Based vs Model-Based – The Real Enterprise Trade-off
Here’s a concrete architectural AI agents vs AI models table for enterprise teams.
Table: Model-Based vs Agent-Based AI Architecture
| Dimension | Model-Based Architecture | Agent-Based Architecture |
| Core Unit | Single model inference | One or more agentic LLMs |
| Behavior Pattern | Input → Output | Observation → action loop with memory |
| Workflow Type | Linear pipeline | agentic workflow automation |
| Orchestration | Hardcoded DAG/scripts | Dynamic AI orchestration |
| Memory | Ad-hoc caching or RAG | Structured agent state management using vector DBs & knowledge graphs |
| Tools & APIs | Called by app logic | Called by tool-using agents |
| Autonomy | Manual supervision | Graduated AI autonomy levels |
| Evolution | Re-train or fine-tune | Self-improving agents via feedback |
| Scale Pattern | Add more endpoints | Add more agents & tools (horizontal multi-agent collaboration) |
| Typical Fit | Analytics, scoring, assistive UX | End-to-end AI planning & execution |
In short:
Model-based is about answers.
Agent-based is about outcomes.
Note: When you confuse them, your architecture drifts.
How the Wrong Architecture Creates Engineering Debt?
Now let’s talk about the debt you asked about specifically: what goes wrong when you try to get agentic behavior from a model-only setup.
Integration & Orchestration Debt
Teams start with a simple LLM call. Then:
- Need to call three tools → add if/else logic
- Need retries → add loops
- Need to “remember” context → bolt on a vector DB
- Need conditional branching → build an orchestrator service
Within months, you’ve hand-rolled a partial AI agent architecture inside an app that was only supposed to call a model.
Articles on agentic AI workflow architecture and agentic AI orchestration show this pattern repeatedly: enterprises write orchestration code manually when they should be using platforms designed for workflow orchestration and autonomous decision pipelines.
This glue code becomes:
- Hard to debug
- Hard to extend to new use cases
- Tightly coupled to a single vendor or model
Data, Memory & State Debt
Agents need:
- Short-term “scratchpad” memory for chain-of-thought reasoning
- Long-term memory for user, task, and environment state
- Structured knowledge via knowledge graphs or other stores
When teams layer this on reactively, they produce partial solutions like:
- RAG bolted to a stateless model
- Session variables used as pseudo-memory
- Ad-hoc logs used as “history.”
Over time, this creates:
- Untraceable state transitions
- Difficulty in reproducing decisions
- Governance gaps (who changed what, and why?)
A proper agent-based AI architecture vs model-based AI design treats memory as a first-class concern.
Ops & Cost Debt
Because bare models don’t plan or act, teams call them over and over to simulate an agent:
- “Now summarize this…”
- “Now decide the next step…”
- “Now rewrite that output…”
OpenAI’s own work on tool use and recent “deep research” style systems shows that when you promote the agentic loop to a first-class citizen, you can dramatically reduce redundant calls while increasing task success.
Governance & Risk Debt
Regulators and standards bodies (e.g., NIST AI RMF, ISO/IEC 42001) increasingly expect:
- Traceability of decisions
- Clear separation of policy vs execution
- Guardrails on autonomous systems
Awareness Tip: Agent-aware design lets you place checks at the agent level, not every endpoint, and align with governance expectations more cleanly.
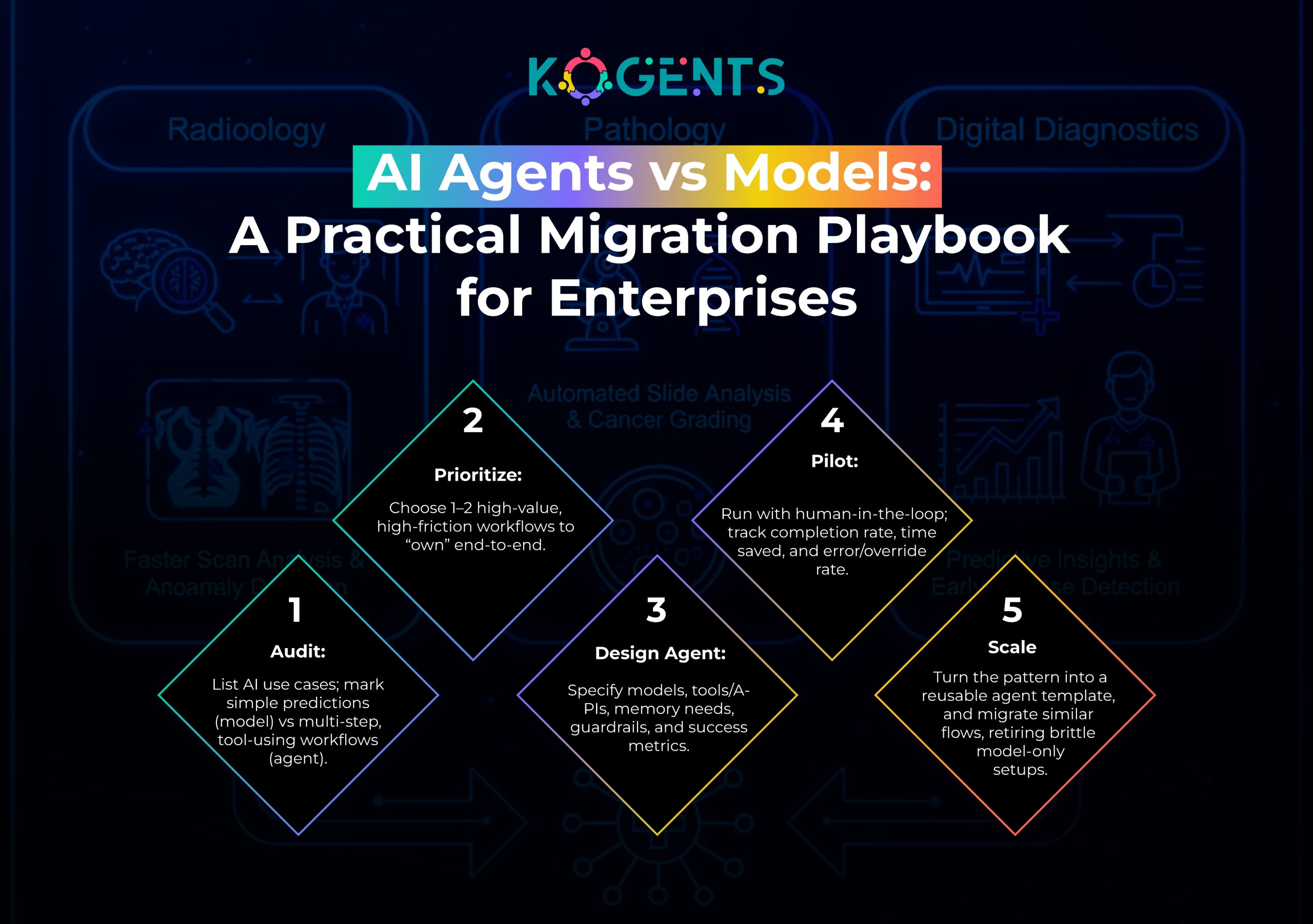
Used Cases: Agents vs Models in Practice
Let’s look at three distinct AI automation examples that clarify how LLM agents vs foundation models play out in real systems.
Microsoft AutoGen: Multi-Agent Systems for Complex Tasks
Microsoft Research’s AutoGen framework shows how you can build a multi-agent system vs a single model setup, where:
Key lesson:
- A single model can’t reliably self-critique and tool-use at scale
- A multi-agent collaboration with explicit roles and environment interaction loops completes more complex tasks with higher reliability
- Trying to emulate this with one “super prompt” is fragile and expensive.
Stanford “Generative Agents”: Simulated Town with Human-Like Behavior
Stanford’s “Generative Agents: Interactive Simulacra of Human Behavior” populates a small town with 25 agents who live, plan, socialize, and coordinate a Valentine’s Day party, entirely autonomously.
The architecture combines:
- LLM-based reasoning
- Long-term memory
- Reflection and planning
- Simulation of a shared environment
This is a living example of:
- agent-based simulations
- emergent behaviors in AI
- goal-driven AI behavior
McKinsey on Agentic AI Advantage in Complex Business Processes
McKinsey’s 2025 insight on agentic AI advantage argues that true value comes from custom-built agents aligned with a company’s core value levers, such as adaptive supply chains or end-to-end customer resolution.
This is where:
- Model-centric AI vs agentic AI becomes a CFO-level decision, not just an engineering one
- You design autonomous decision pipelines around your business processes, rather than sprinkling models into existing tools.
A Practical Framework: When Do You Need an Agent, Not Just a Model?
Here’s a simple decision tree you can use.
Ask about each use case:
- Is the task single-step or multi-step?
- Single: classification, one-shot generation → a model may be enough.
- Multi: “research → decide → act → verify” → you need to Automate with AI Agents
- Does the system need to call tools or move data between systems?
- If yes, you’re in the tool-using agents’ territory
- Does success depend on context over time?
- If yes, you need agent state management and memory, not just prompts
- Do you want the system to adapt its behavior over time?
- If yes, you’re heading toward self-improving agents with policy optimization, RL, or RLHF
Read It: If you answer “yes” to #2–4, you’re not just selecting a model; you’re designing an AI agent architecture.
Getting AI Architecture Right Is Now a Strategic Advantage
Confusing AI agents vs AI models leads to brittle workflows, hidden costs, and re-platforming, the true shape of your future engineering debt.
The next decade won’t be won by who has the biggest foundation model, but by who has the most robust agentic AI architecture tied to their core processes.
Avoid Architecture Debt, and build Agentic AI with the best agentic AI company, Kogents.ai
If you’re serious about:
- Automating real work, not just generating text
- Designing agentic workflows instead of fragile prompt spaghetti
- Aligning AI behavior with your data, policies, and value levers
Kogents.ai gives you:
- Opinionated AI agent architecture for enterprises
- Native workflow orchestration and tool integration
- Multi-agent patterns without hand-rolling frameworks
- Governance and observability to keep agents aligned
Build resilient, future-proof AI systems: architects with agents, not just models — with us at the center.
FAQs
What is the core difference between an AI model and an AI agent?
An AI model is a predictive function: given input, it outputs a result once. An AI agent wraps one or more models in a loop that observes state, reasons, chooses actions, calls tools, and reacts to feedback. The agent’s job is to achieve a goal; the model’s job is to provide predictions or content along the way.
Are AI agents always built on top of LLMs?
Not always, but most modern enterprise agents use large language models (LLMs) as their main reasoning engines. They may combine LLMs with classic ML models, rules, and simulations. The key is that the agent owns the decision-making algorithms, AI planning & execution, and agent state management — not the underlying model.
Why does using only models create engineering and architecture debt?
When you use models to handle workflows that require autonomy, you end up writing orchestration logic yourself: routing, retries, memory, tool calls, and approvals. Over time, this “glue code” grows into a custom, undocumented agentic AI framework that your team never meant to build — which becomes costly to maintain, extend, and audit.
How do I know if my use case needs an agent instead of just a model?
Ask whether the system must: (1) perform multi-step reasoning, (2) call multiple tools/APIs, (3) track context across time, and (4) adapt based on environment feedback. If the answer is yes to more than one, you’re in agentic AI territory. Use a model for a step; use an agent for an outcome.
What are “agentic workflows” in practical terms?
Agentic workflows are processes where agents dynamically decide which steps to execute to reach a goal, rather than following a fixed, hardcoded path. For example, instead of a rigid script for handling a support ticket, an agent might read context, search knowledge bases, call tools, request human approval when needed, and close the ticket — all as part of an autonomous workflow.
Are multi-agent systems just hype, or do they add real value?
Multi-agent systems add real value in complex tasks: coding, research, planning, and simulations. Systems like AutoGen and Generative Agents show that specialized agents (planner, executor, critic, verifier) collaborating often outperform a single, general-purpose model. They can reduce hallucinations, improve coverage, and better reflect real-world team structures.
How do agent architectures fit with AI governance and safety?
Agents give you natural “hooks” for governance: you can insert policies at the agent level (e.g., “never execute this type of action without human approval”), log decisions, and separate policy optimization from raw inference. This lines up well with frameworks like NIST AI RMF and ISO/IEC 42001, which emphasize traceability and control over autonomous systems.
Does using agents mean higher cloud costs?
Not automatically. Poorly designed agents that call models too often can be costly. But well-architected agents usually reduce waste by reusing context, avoiding redundant calls, and coordinating steps more intelligently. What you gain in reduced failures, human intervention, and rework often outweighs any additional overhead from the agentic loop itself.
How do RLHF and reinforcement learning relate to agents?
RLHF (reinforcement learning from human feedback) and reinforcement learning agents provide mechanisms for making agents self-improving over time. Instead of hardcoding all behavior, you let the system learn which action sequences perform best under real-world feedback. This is especially valuable in dynamic environments like customer support or operations.
Where should a company start if it wants to move from model-centric to agentic AI?
Start with one or two high-impact workflows where humans are currently orchestrating many steps (e.g., customer resolution, onboarding, underwriting). Map the process, identify tools and systems, and then design a pilot agent that handles a constrained portion of the workflow with human oversight.




 AI Agents vs Workflows — The Core Differences
AI Agents vs Workflows — The Core Differences