This statistical fact clearly depicts that the future of medicine is digital, and at its core lies Software as a Medical Device (SaMD), an emerging category of regulated software that performs medical functions without being part of a physical device.
From AI-powered imaging diagnostics to digital stethoscopes and mental health monitoring apps, SaMD is transforming how clinicians diagnose, predict, and personalize treatment.
For entrepreneurs and solopreneurs in health tech, the opportunity is massive, but so is the regulatory responsibility.
Developing AI SaMD requires mastering compliance, building trust with regulators like the FDA and European Commission, and maintaining consistent performance post-deployment.
The foundation for achieving this is compliant MLOps, a framework that unites machine learning development, regulatory governance, and post-market monitoring into a single, auditable lifecycle.
This guide breaks down everything you need to know about developing AI Software as a Medical Device, how to implement compliant MLOps pipelines, and how to ensure your solution meets global regulatory standards while remaining agile and innovative.
Key Takeaways
- Software as a Medical Device (SaMD) is revolutionizing healthcare through AI and digital innovation.
- Compliance and quality management aren’t optional; they’re the backbone of trust.
- MLOps for AI SaMD ensures traceability, validation, and continuous monitoring.
- Post-market vigilance guarantees patient safety and regulatory confidence.
- For entrepreneurs, early adoption of compliance frameworks translates into faster approvals and sustainable growth.
Decode The Term: Software as a Medical Device (SaMD)?
The International Medical Device Regulators Forum (IMDRF) defines Software as a Medical Device (SaMD) as “software intended to be used for one or more medical purposes that perform these purposes without being part of a hardware medical device.”
SaMD vs. SiMD
It’s important to distinguish between:
- SaMD (Software as a Medical Device): Standalone software like an AI radiology model, remote health monitoring tool, or mental health app.
- SiMD (Software in a Medical Device): Embedded software inside a device, such as firmware in an insulin pump.
Regulatory Frameworks
Different regions define and regulate SaMD differently:
- United States (FDA): Overseen by the Center for Devices and Radiological Health (CDRH). Submissions fall under 510(k), De Novo, or PMA pathways.
- European Union (EU MDR): Defines “Medical Device Software (MDSW)” under MDR Article 2. Classification is risk-based (Class I–III) depending on intended use.
- IMDRF: Provides global harmonization through risk-based frameworks and clinical evaluation guidance.
Examples of SaMD
- Aidoc – AI imaging triage tool cleared by FDA.
- Eko Health – Digital stethoscope with AI for cardiac analysis.
- Caption Health – AI for ultrasound guidance.
Note: These examples prove that software alone, when properly validated and regulated, can truly become a clinical-grade medical device.

The Rise of AI in SaMD Development
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has accelerated the SaMD landscape, enabling predictive AI doctor diagnosis and real-time patient insights.
AI and Machine Learning (ML) models can detect subtle patterns invisible to human eyes, powering clinical decision support (CDS) tools and automated diagnostics.
However, AI also introduces complexity. Unlike static rule-based software, AI models learn and evolve.
A model that performs well today might degrade tomorrow if data distributions change, a phenomenon known as data drift.
That’s why regulators require strong governance over every step of the AI lifecycle.
| To manage this, the FDA, IMDRF, and WHO are promoting Good Machine Learning Practice (GMLP) principles for data quality, transparency, reproducibility, and monitoring. |
GMLP bridges AI innovation and regulatory reliability.
In essence, AI SaMD = Software + AI Model + Medical Purpose + Regulation.
The secret to sustaining this equilibrium lies in compliant MLOps, the operational discipline that ensures ML systems are built, deployed, and maintained under quality management and regulatory control.
Regulatory Foundations for SaMD
- Developing SaMD is not just about writing code; it’s about engineering trust.
- Regulators demand that every software component be traceable, validated, and risk-managed.
Let’s explore the foundational standards that guide this process.
Core SaMD Standards
| Standard | Purpose |
| IEC 62304 | Defines the software life-cycle processes for medical device software. Covers design, implementation, verification, and maintenance. |
| ISO 14971 | Focuses on risk management for medical devices — identifying, evaluating, and mitigating hazards. |
| ISO 13485 | Defines quality management systems (QMS) specific to medical device organizations. |
| IEC 82304-1 | Addresses health software product safety and security. |
| ISO/IEC 27001 | Manages data security and integrity, critical for clinical datasets. |
Key Regulatory Elements
- Intended Use – Clearly define the medical purpose.
- Risk Classification – Based on AI patient scheduling impact.
- Design Controls – Traceability from requirements → implementation → verification.
- Validation & Verification (V&V) – Ensures that the software meets its intended use.
- Clinical Evaluation – Demonstrate safety and performance through evidence.
- Post-Market Surveillance (PMS) – Monitor and report performance post-deployment.
Pro Tip: Start with IEC 62304 mapping early, as even small startups can embed traceability and risk management into their Git workflows with tools like Greenlight Guru or Orcanos QMS.
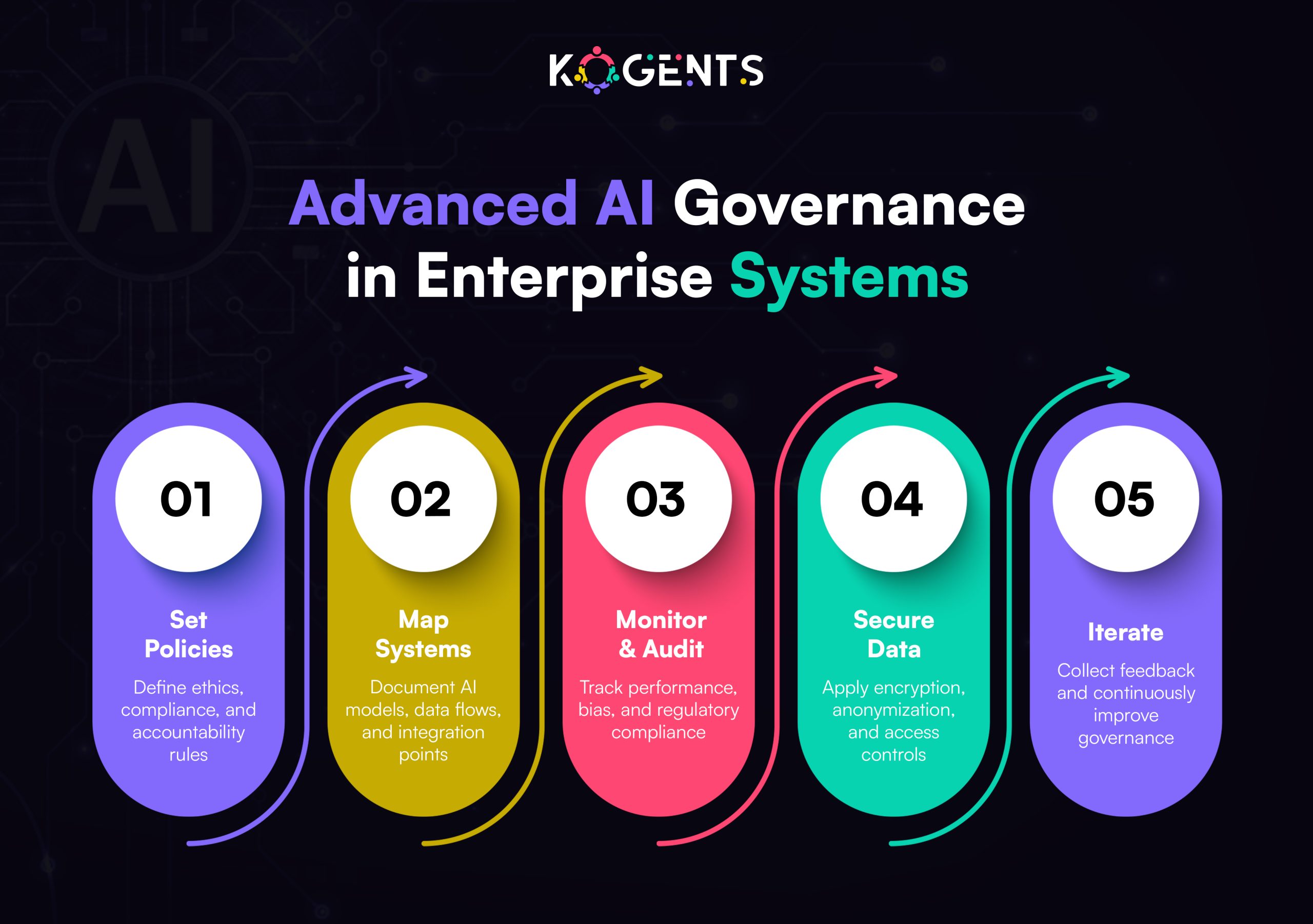
Building Compliant MLOps Pipelines for AI SaMD
MLOps (Machine Learning Operations) applies DevOps principles to ML development, but in regulated environments, it also embeds compliance, validation, and quality management.
A compliant MLOps pipeline ensures every dataset, model version, and metric powering AI agents for healthcare automation is traceable, validated, and reproducible.
Key Components of Compliant MLOps
- Data Governance & Lineage
- Maintain detailed records of dataset sources, preprocessing steps, and labeling methods.
- Use data versioning tools (like DVC or MLflow) integrated with QMS for audit readiness.
- Model Version Control & Traceability
- Every model iteration must link back to specific training data, hyperparameters, and validation results.
- Maintain a Model Card summarizing performance, limitations, and clinical use conditions.
- Validation & Verification Automation
- Automate unit, integration, and regression testing.
- Integrate automated pipelines with Design Review and Risk Management checkpoints.
- Change Management
- Document every change affecting safety or performance.
- Follow the FDA’s Predetermined Change Control Plan (PCCP) for AI models that evolve post-approval.
- Auditability & Reproducibility
- Store logs, metrics, and artifacts to enable end-to-end audit trails for regulators.
Compliant MLOps Tools
- MLflow / Kubeflow for experiment tracking.
- Greenlight Guru for medical QMS integration.
- Azure ML, AWS SageMaker, or GCP Vertex AI with compliance configurations.
Continuous Monitoring and Post-Market Surveillance
Once your AI SaMD is deployed, your compliance journey doesn’t end; it begins. Regulators expect post-market surveillance (PMS) to ensure continued safety, performance, and real-world accuracy.
Post-Market Monitoring in Practice
- Performance Drift Monitoring: Track accuracy, precision, sensitivity/specificity over time.
- Data Drift Detection: Monitor input data for shifts in distribution or quality.
- Bias Detection: Evaluate demographic fairness continuously.
- Adverse Event Reporting: Log and report incidents as per regulatory timelines.
- Explainability Tracking: Ensure clinicians understand AI outputs.
Automation Opportunities
Integrate monitoring into MLOps dashboards:
- Trigger alerts when metrics drop below thresholds.
- Automate retraining workflows under a controlled, validated process.
- Generate Regulatory PMS Reports periodically.
Global Best Practices
Both the FDA and EU MDR emphasize continuous oversight, not one-time approval. The FDA’s Total Product Lifecycle (TPLC) framework aligns perfectly with this model, blending pre-market validation with post-market vigilance.
Challenges and Pitfalls in AI SaMD Development
Even the best teams face challenges in balancing innovation with compliance.
Common Challenges
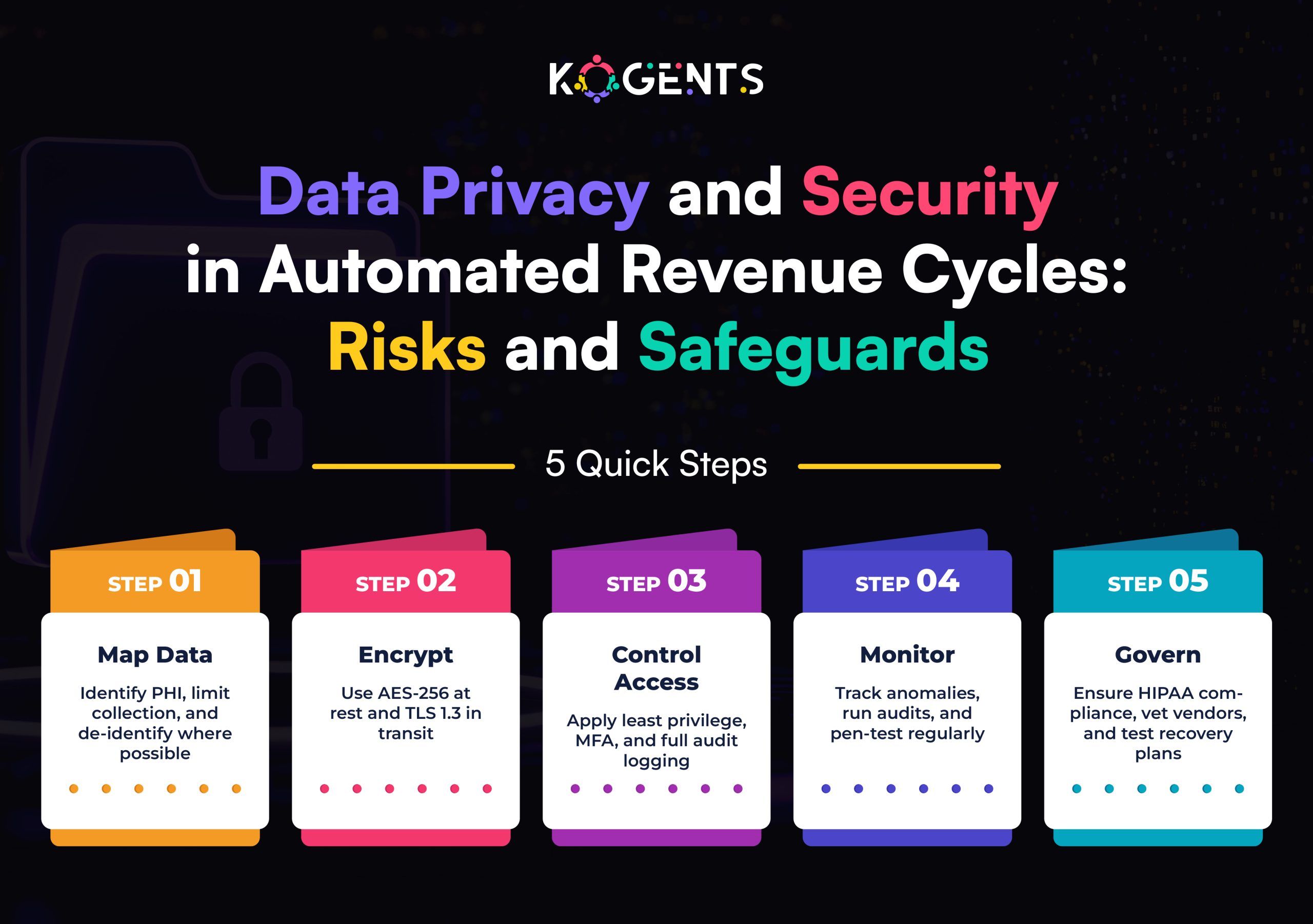
- Data Scarcity and Privacy Constraints
- Medical datasets are limited and often fragmented.
- Compliance with HIPAA (US) and GDPR (EU) is mandatory.
- Algorithmic Bias and Explainability
- Black-box models risk clinical mistrust. Regulators demand transparency.
- Validation Across Environments
- Models must generalize across clinical settings, devices, and populations.
- Interoperability Barriers
- Integration with hospital EHRs (Epic, Cerner, FHIR APIs) can be complex.
- High Regulatory Costs
- Verification, documentation, and QMS setup require upfront investment.
Avoid These Compliance Mistakes
|
Soft Reminder: Adopt a “compliance-by-design” approach, embed validation gates within your CI/CD pipelines rather than adding them later.
AI SaMD vs. Traditional Medical Software
| Aspect | Traditional Medical Software | AI-Enabled SaMD |
| Decision Logic | Rule-based, deterministic | Data-driven, adaptive |
| Regulation Model | Fixed function validation | Continuous oversight required |
| Validation Process | One-time premarket validation | Continuous validation & monitoring |
| Risk Management | Stable | Dynamic (requires active reclassification for updates) |
| Maintenance | Periodic updates | Continuous learning and retraining |
| Oversight | Manual | Automated through MLOps & audit trails |
| Transparency | Clear logic flow | Requires model explainability tools |
Case Study Spotlight: From Startup to FDA Clearance
Case: Aidoc — AI Imaging Diagnostics
Aidoc, founded in Israel, built an AI-based diagnostic platform that helps radiologists detect critical findings in CT scans. Its journey offers a masterclass in AI SaMD lifecycle excellence.
- Intended Use: Assist radiologists by prioritizing scans with potential abnormalities.
- Risk Classification: Moderate risk (FDA Class II).
- Clinical Data Pipeline: Trained on millions of de-identified medical images under HIPAA compliance.
- Model Validation: Conducted multi-site clinical trials to prove sensitivity/specificity.
- Regulatory Submission: Submitted through the FDA’s 510(k) pathway.
- Post-Market Surveillance: Continuous model performance tracking with real-time dashboards.
Result: Aidoc became one of the first AI radiology SaMDs cleared by the FDA, setting a precedent for AI-enabled diagnostics worldwide.
| Takeaway for Entrepreneurs: Invest early in compliance infrastructure. Aidoc didn’t treat validation as an afterthought; it built compliance into its product DNA. |
Best Practices & ROI for Entrepreneurs and Solopreneurs
For founders entering the medical AI space, compliance can seem overwhelming. But early adherence to SaMD best practices can save time, money, and regulatory pain later.
Top Best Practices
- Start with intended use clarity: Your regulatory pathway depends on it.
- Build a minimal QMS early: Even small startups can use templates aligned to ISO 13485.
- Implement traceability from day one: Link code commits to design controls and risk items.
- Use validated tools: Only deploy AI models in qualified cloud environments.
- Engage regulatory consultants: They can shorten approval cycles dramatically.
Mini Case Example: A digital pathology startup using compliant MLOps reduced its FDA submission cycle from 18 months to 12 months, saving over $500,000 in development delays.
The Future of AI Software as a Medical Device
The next generation of SaMD will be adaptive, interoperable, and context-aware. Regulators are already preparing for this evolution.
Emerging Trends
- Adaptive AI Regulation: FDA’s forthcoming framework for continuously learning models.
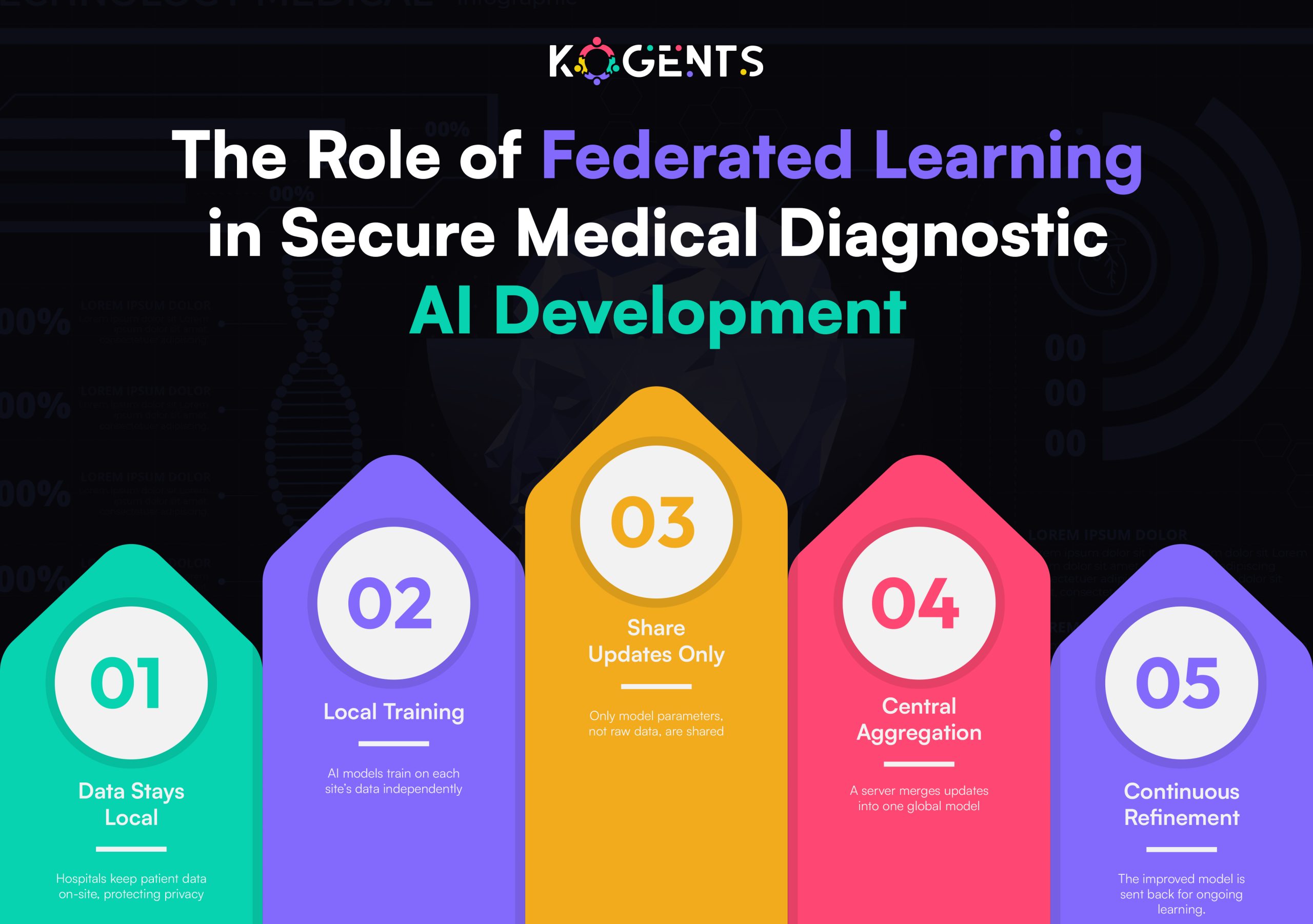
- Federated Learning: Privacy-preserving model training across hospitals.
- Real-World Evidence (RWE): Using real-world performance data for post-market validation.
- FHIR & HL7 Integration: Seamless exchange between SaMD and EHR systems.
- Global Harmonization: IMDRF, WHO, and regional bodies aligning AI medical device standards.
Pro Tip: Compliance is not bureaucracy; it’s a competitive advantage in winning trust, funding, and regulatory approval.

Before You Leave!
The line between software and medical device has blurred, and for good reason. As AI Software as a Medical Device becomes central to modern medicine, entrepreneurs who embrace compliant MLOps and continuous monitoring will define the future of digital health.
Building SaMD isn’t just about compliance; it’s about saving lives with software that’s safe, effective, and transparent.
Whether you’re a solopreneur developing a diagnostic app or a startup founder scaling AI in healthcare, regulatory alignment will amplify your innovation, not hinder it.
Look how Kogents.ai empowers entrepreneurs, solopreneurs, and healthcare providers to build compliant AI medical devices.
FAQs
How do you ensure continuous monitoring after SaMD deployment?
Post-market surveillance (PMS) includes monitoring data and performance drift, detecting bias, logging adverse events, and generating periodic regulatory reports. Automation in MLOps pipelines enables real-time alerts and retraining workflows.
What are the common challenges in developing AI-based SaMD?
Challenges include limited clinical datasets, data privacy (HIPAA, GDPR), algorithmic bias, validation across multiple environments, interoperability with EHRs, and high regulatory costs.
What is the difference between traditional medical software and AI-enabled SaMD?
Traditional software uses fixed, rule-based logic and requires one-time validation.
AI-enabled SaMD is adaptive, requiring continuous validation, risk reassessment, and ongoing monitoring for fairness and reliability.
What is Software as a Medical Device (SaMD)?
SaMD refers to software that performs medical functions — such as diagnosis, monitoring, or treatment — without being part of a physical medical device. Examples include AI imaging tools, digital stethoscopes, and mental health monitoring apps.
How is SaMD different from Software in a Medical Device (SiMD)?
SaMD operates independently of hardware, like an AI-based radiology model. SiMD, on the other hand, is embedded in a physical device, such as firmware in an insulin pump.