The accelerating convergence of Healthcare with AI, genomic intelligence, and precision medicine is redefining how diseases are diagnosed, treated, and prevented.
Artificial intelligence is no longer just augmenting clinical workflows; it is functioning as a scientific multiplier, uncovering patterns in biological data that were once invisible to human experts.
Combined with genomic sequencing and computational biology, AI is turning healthcare from a reactive system into a predictive, preventative, and hyper-personalized care ecosystem.
Today’s most advanced hospitals, research centers, and biotech innovators are leveraging machine learning models, predictive analytics, natural language processing, and healthcare AI agents to decode genomic markers, optimize treatment pathways, and forecast disease trajectories.
Meanwhile, AI algorithms integrate clinical notes, EHRs, medical imaging, lab reports, and multi-omics data to generate personalized therapeutic recommendations with unprecedented precision.
Key Takeaways
- AI Agents for Healthcare Automation and genomics are shifting medicine from symptom-based to biological-level precision, enabling individualized risk assessment, early detection, and targeted therapeutic interventions.
- Machine learning–driven multi-modal data fusion allows clinicians to integrate imaging, genetics, labs, and lifestyle data into cohesive clinical insights.
- Genomic intelligence provides the molecular blueprint for precision medicine, enabling AI to match the right drug to the right patient at the right time.
- AI elevates operational, clinical, and research efficiency, improving diagnostic accuracy, reducing administrative workload, and accelerating drug discovery.
- The next decade will bring AI-powered digital twins, computational clinical trials, genome-guided vaccines, and autonomous diagnostic ecosystems.
Understanding Healthcare with AI & Expanded Genomic Intelligence
Genomic intelligence refers to the computational interpretation of a person’s genome (DNA), transcriptome (RNA), proteome, metabolome, and polygenic risk scores.
When paired with artificial intelligence, this enables clinicians to decode:
- Hereditary susceptibility to disease
- molecular pathways driving patient-specific conditions
- drug–gene interactions and therapeutic resistance
- tumor evolution patterns
- gene expression signatures predicting prognosis
Why Does AI Matters in Genomics More Than Ever?
The volume and complexity of data limit human interpretation of genomic sequences. A single whole genome contains over 3 billion base pairs, far beyond manual analysis.
AI simplifies this by:
1. Identifying pathogenic variants at scale
Deep learning models categorize harmful mutations, structural variants, epigenetic modifications, and copy-number variations.
2. Modeling how variants impact biological pathways
AI predicts protein folding, molecular interactions, and phenotypic expression shifts.
3. Matching genomic markers to targeted therapies
For example:
- BRCA1/2 → PARP inhibitors
- HER2 amplification → Trastuzumab
- EGFR mutations → Osimertinib
4. Accelerating genomic report-generation
AI reduces genomic analysis time from days/weeks to minutes, essential during critical care or cancer staging.
5. Predicting long-term risk using polygenic risk scoring (PRS)
AI-enhanced PRS predicts lifetime susceptibility to:
- cardiovascular disease
- type 2 diabetes
- Alzheimer’s
- various cancers
The integration of genomic intelligence with predictive analytics in healthcare marks a shift from generalized medicine to precision-first interventions.

Clinical Applications Across Specialty Areas
1. Oncology: AI-Driven Tumor Biology & Precision Oncology
Modern cancer care heavily relies on healthcare AI assistants pitching AI-enhanced genomic profiling.
AI in oncology enables:
- Discovery of tumor-specific driver mutations
- prediction of treatment response to immunotherapy
- real-time monitoring of tumor evolution via liquid biopsy
- personalized drug-matching based on genomic signatures
A study in Nature Communications found “actionable mutation detection” vs traditional pathology workflows. Rather, it evaluates computational methods for identifying cancer driver mutations and validates certain variants of unknown significance (VUSs) as pathogenic through patient survival data.
AI tools also identify biomarkers for immunotherapy response, such as tumor mutational burden (TMB) and neoantigen load.
2. Cardiology: AI Predicts Cardiovascular Events Years Ahead
AI interprets imaging + genomic risk to forecast major cardiovascular events.
Key use cases:
- Predicting atrial fibrillation 5 years before onset
- identifying high-risk familial hypercholesterolemia via genome screening
- Detecting asymptomatic cardiomyopathy from EKG waveforms
- forecasting heart failure using multi-modal data
3. Neurology: AI for Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s & Neurogenetics
Neurological disorders often begin decades before symptoms. AI helps identify:
- early amyloid/tau accumulation
- genomic risk for Alzheimer’s (APOE4 variants)
- motor decline patterns
- brain imaging biomarkers
4. Infectious Diseases: Genomics + AI for Outbreak Prediction
AI enables genomic epidemiology to:
- track viral mutations
- model drug resistance
- Predict patient-specific immune response.
- Optimize vaccine design
Insight: During COVID-19, AI tools modeled genomic variation to accelerate mRNA vaccine development.
5. Rare Diseases: Reducing Diagnostic Time from Years to Weeks
Rare genetic disorders often take 5–7 years to diagnose.
AI shortens this by analyzing:
- phenotype descriptions
- whole-genome sequences
- clinical imaging
- biochemical markers
Case in Point: Boston Children’s Hospital reported an 80% reduction in diagnostic time using AI-driven genomics for rare pediatric conditions.
6. Pharmacogenomics: AI for Personalized Drug Selection
AI evaluates how genes impact drug metabolism (CYP450 variants), toxicity risk, and therapeutic response.
Benefits include:
- Fewer adverse drug events
- optimized dosage
- reduced trial-and-error prescribing
- Higher adherence and improved clinical outcomes
AI-Enabled Multi-Modal Data Fusion in Precision Medicine
Multi-modal data fusion is one of the most powerful innovations shaping Healthcare with AI. It combines:
- genomics
- imaging
- EHR
- clinical notes
- proteomics
- metabolomics
- wearable sensor data
- pathology slides
Key Note: AI integrates these diverse datasets into a unified clinical insight model.
Why is Multi-Modal AI a Breakthrough?
- Holistic Patient Understanding: A complete biological + clinical portrait is created, leading to extremely accurate treatment strategies.
- Superior Predictive Power: Combining genomic + imaging data increases diagnostic accuracy massively, per a 2023 Nature meta-study.
- Continuous Learning from Real-Time Data: Wearables, remote monitors, and sensors update models dynamically.
- Improved Treatment Matchmaking: AI identifies which therapy works best for each biological subtype of a disease.
- Faster Diagnosis & Reduced Cost: Data fusion reduces redundant tests and misdiagnoses.
Next-Gen Healthcare Infrastructure Powered by AI
To support AI-driven clinical care, healthcare systems are evolving into AI-native infrastructures that include:
1. Digital Diagnostics Hubs
Automated AI centers that:
- run imaging
- genomic analysis
- pathology interpretation
- risk prediction
These hubs reduce diagnostic cycle time from weeks to hours.
2. Ambient Clinical Intelligence (ACI)
Tools like Nuance’s DAX Copilot enable automated clinical documentation, reducing clinician burnout and ensuring accurate EHR input.
3. AI-Powered Clinical Command Centers
Hospitals use digital “mission control” centers for:
- bed allocation
- patient flow optimization
- ICU monitoring
- real-time triage
4. Virtual Care & Remote Monitoring Ecosystems
AI voice agents for healthcare analyze wearable sensor data for early risk detection, but only when they are integrated with a patient’s health data ecosystem.
Examples:
- arrhythmia prediction
- glucose instability forecasting
- Sleep Apnea Detection
- respiratory distress monitoring
Case Studies in AI-Driven Precision Medicine
Case Study 1: Tempus AI for Genomic-Driven Oncology
Tempus uses AI + genomic sequencing to personalize cancer therapy.
Key Results:
- Over 2.2 million clinical records and 700,000 genomic profiles analyzed
- AI identified optimal therapy options up to 45% faster
- Improved survival outcomes in lung and breast cancer cohorts
Case Study 2: NYU Langone’s NYUTron LLM for Hospitalized Patients
NYU Langone created NYUTron, an LLM trained on EHR data.
Key Results:
- Predicted 30-day readmission with 81% accuracy
- Reduced discharge delays by 20%
- Provided actionable clinical insights during rounds
Win-Win Situation: This validated LLM point-of-care deployment marks a major milestone in clinical AI.
Case Study 3: Oxford Nanopore + AI for Rapid Infectious Disease Genomics
AI + Oxford nanopore sequencing enabled real-time pathogen identification.
Key Results:
- Sequencing turnaround reduced from 24 hours to <90 minutes
- Crucial in ICU sepsis cases where time is critical
- Enabled targeted antimicrobial therapy, reducing mortality
Case Study 4: DeepMind’s AlphaFold for Protein Structure Prediction
AlphaFold predicted proteins with atomic-level accuracy, revolutionizing drug discovery.
Key Results:
- Solved over 200 million protein structures
- Accelerated novel drug discovery pipelines worldwide
- Reduced structural biology research timelines from years to hours
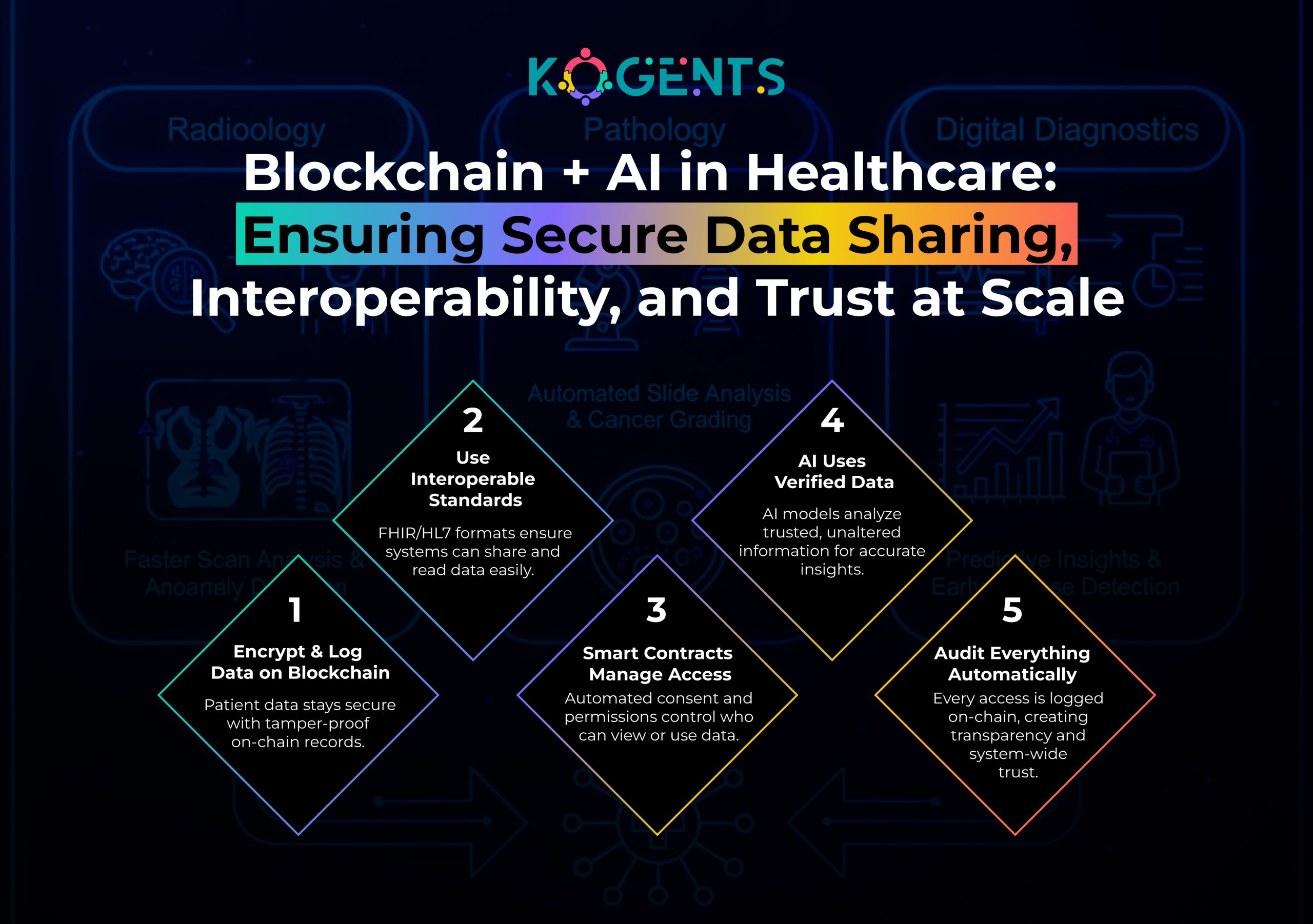
Future of Healthcare with AI & Genomic Intelligence
The next decade of Healthcare with AI will be defined by breakthroughs that make personalized medicine the global standard.
1. AI-Generated Digital Twins for Patients
Digital replicas simulate a patient’s heart, brain, tumors, or entire physiology.
- Siemens Healthineers predicts digital twins will reduce cardiac treatment complications by half.
- Used for drug testing, surgery planning, and predicting disease progression.
2. AI-Powered Genome Editing & CRISPR Optimization
AI models optimize CRISPR edits by predicting:
- off-target effects
- optimal guide RNA sequences
- gene–protein interactions
3. Computational Clinical Trials
AI simulates trial outcomes, reducing:
- trial duration
- recruitment size
- cost
4. Fully Autonomous Diagnostic Ecosystems
End-to-end AI diagnostic centers will integrate:
- AI imaging
- genomic analysis
- lab automation
- digital pathology
5. Genome-Guided Vaccines & Personalized Immunotherapy
AI will design vaccines tailored to individual immune systems.
6. Multi-Omics Precision Platforms
Future hospitals will use integrated:
- genomics
- proteomics
- metabolomics
- microbiome data
- exposomics
AI fuses these into personalized health scores and early-warning analytics.
7. Predictive-First Healthcare Systems
Instead of waiting for sickness:
- AI predicts heart disease 5–10 years early
- Genomics predicts cancer susceptibility
- Wearables forecast acute events
McKinsey estimates predictive healthcare could save $1 trillion annually in global medical costs.
AI vs. Traditional Healthcare Precision Capabilities
| Feature | Traditional Healthcare | AI-Driven Precision Healthcare |
| Disease Detection | Reactive; symptoms-based | Predictive; early risk identification |
| Data Processing | Manual; limited | Automated; handles millions of records |
| Genomic Interpretation | Slow; specialist-dependent | Instant genomic pattern analysis |
| Treatment Personalization | Generalized protocols | Hyper-personalized; genome-dependent |
| Clinical Decision-Making | Human intuition only | AI-assisted; evidence-driven |
| Diagnostic Speed | Hours–weeks | Seconds–minutes |
| Error Rate | High variability | Reduced through ML accuracy |
Wrapping Up!
The convergence of Healthcare with AI and advanced genomic intelligence is redefining the future of medicine, shifting care from generalized treatment to precision-driven, biologically informed interventions.
As AI continues to decode complex genomic patterns, anticipate disease trajectories, and elevate clinical decision-making, healthcare systems are entering an era where diagnosis is earlier, therapies are hyper-personalized, and outcomes are significantly improved.
This is not just innovation, it’s a foundational transformation in how medical care is delivered.
For healthcare organizations, biotech teams, and digital-first medical innovators, succeeding in this new landscape requires more than advanced treatments; it demands a strong digital presence that conveys authority, accuracy, and trust.
Kogents.ai empowers you to build that presence. We help you elevate your brand as a leader in healthcare innovation if you’re ready to position your organization at the forefront of AI-driven precision medicine.
Partner with us where expertise meets intelligent growth.
FAQs
What is Healthcare with AI, and how does it improve medical accuracy?
Healthcare with AI leverages machine learning models, predictive analytics, and computer vision to detect diseases earlier and enhance diagnostic accuracy. AI evaluates millions of data points—clinical records, genomic markers, imaging, and lab results—to provide reliable predictions. This reduces diagnostic errors and supports clinicians with evidence-backed decision-making.
How is AI used in hospitals to improve patient outcomes?
Hospitals use AI in clinical decision-making, automated triage, remote patient monitoring, and AI-powered healthcare systems to enhance patient outcomes. These tools identify risks such as sepsis or cardiac arrest hours earlier than traditional methods. As a result, physicians can intervene faster and more accurately, significantly reducing complications.
What are the top benefits of artificial intelligence in clinical practice?
The benefits of artificial intelligence in clinical practice include early disease prediction, precise diagnosis, reduced administrative burden, and personalized treatment strategies. AI also improves speed and accuracy in medical imaging, billing, coding, and workflow optimization. This allows clinicians to focus more on patient care and less on repetitive tasks.
How does AI help in precision medicine and genomic intelligence?
AI analyzes genomic sequencing to uncover mutation patterns, drug resistance markers, and hereditary risks. By combining this with clinical data, AI builds treatment plans tailored to a patient’s DNA. This approach boosts therapy effectiveness and minimizes adverse reactions, forming the foundation of AI for precision medicine.
What challenges prevent widespread adoption of AI in healthcare?
Despite its potential, AI faces challenges such as data privacy issues, integration difficulties, bias in training datasets, and concerns around regulatory compliance. Healthcare organizations must ensure HIPAA adherence and FDA guidelines before deploying AI tools, which may slow adoption but ensure safety.
How do AI-powered diagnostic tools compare to traditional methods?
AI-powered tools often outperform traditional methods by identifying subtle disease indicators unnoticeable to the human eye. In radiology, for example, AI identifies early-stage tumors with up to 94% accuracy. The combination of computer vision in diagnostics, ML, and deep learning reduces false negatives and enhances treatment planning efficiency.
Are AI healthcare systems safe and FDA-approved?
Many AI-driven healthcare solutions are FDA-approved under 510(k) pathways, ensuring safety, reliability, and clinical efficacy. Regulatory frameworks like the FDA Software Precertification Program and WHO AI governance guidelines provide strict protocols for safe deployment. Compliance with HIPAA, HL7, and SOC 2 further strengthens trust.
How does AI reduce the cost of healthcare operations?
AI cuts costs by automating administrative tasks, optimizing staff scheduling, and improving diagnostic accuracy, which reduces unnecessary procedures. Healthcare automation with AI decreases billing errors, accelerates coding, and reduces patient readmissions. Studies show AI-driven automation can reduce operational costs by up to 30–40%.
What are common AI tools used in modern hospitals today?
Modern hospitals rely on AI platforms like IBM Watson Health, Google DeepMind, NVIDIA Clara, and Microsoft Healthcare Cloud. These tools manage imaging, diagnostics, genomic sequencing, patient monitoring, and predictive analytics. They support decision-making and streamline patient care pathways.
How will AI and genomics shape the future of healthcare delivery?
AI and genomics will create a predictive-first healthcare model where diseases are detected before they develop and treatments are fully personalized. Future innovations will include digital twins, AI-enabled robotic surgeries, genomic vaccines, and ambient intelligence in hospitals. This transformation will redefine how care is delivered worldwide.
