There’s a silent revolution happening inside high-performance tech teams, and most companies don’t realize what’s coming.
For a decade, automation meant bots, rigid, rule-based scripts designed to “click buttons faster.”
But with the rise of LLM-powered, self-directing, autonomous AI agents, the old logic is collapsing.
The paradigm is shifting from:
“Bots that follow scripts”
to
“Agents that think, plan, and adapt.”
This is the defining battle of modern automation: AI Agents vs Bots.
Companies that adopt agentic automation are achieving massive workflow acceleration, cutting operational costs maximum, and reducing engineering load by eliminating endless repetitive tasks.
Meanwhile, teams stuck with traditional bots continue drowning in maintenance, brittle integrations, and workflows that break the moment business logic changes.
This blog unpacks the real difference between AI agents and bots, why this shift matters, and how leading teams are using AI agents vs agentic AI as an unfair competitive advantage.
Key Takeaways
- AI agents surpass bots because they perform multi-step autonomous decision-making, not just scripted tasks.
- Agentic automation eliminates workflow brittleness, enabling self-correcting, context-aware, and flexible task execution.
- High-velocity tech teams gain massive efficiency boosts via contextual reasoning, predictive logic, and autonomous task planning.
- Bots still matter, but only for deterministic, repetitive, or rules-based automation use cases.
- AI agents unlock next-generation enterprise workflows, integrating deeply with multi-agent systems, LLM orchestration frameworks, and enterprise operations.
AI Agents vs Bots — The Modern Automation Divide
Over the last decade, companies have embraced bots, from RPA bots, workflow bots, and API-driven bots to simple chatbots.
These systems automated repetitive processes successfully, but were limited by their rules-based automation nature.
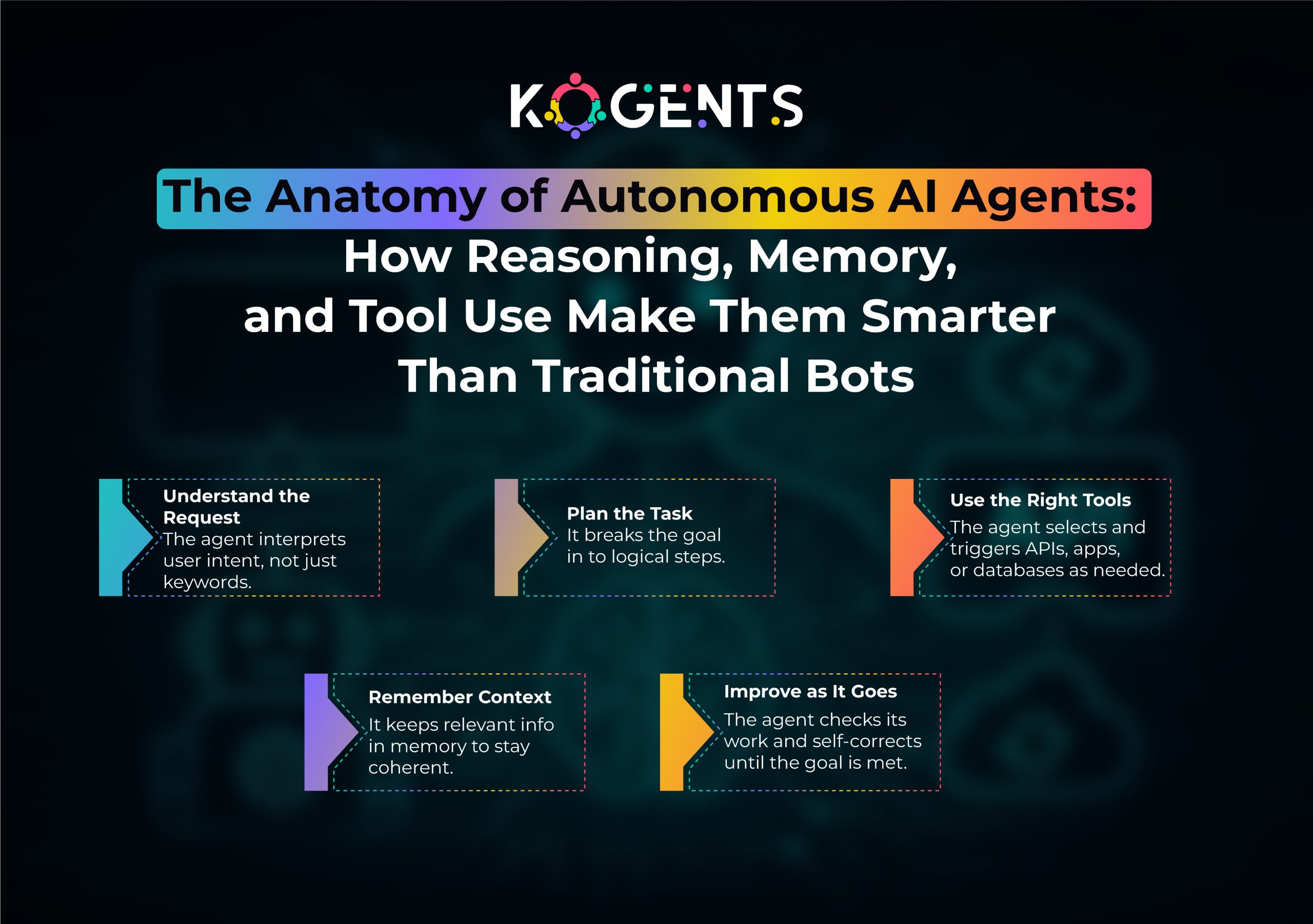
Today’s shift toward AI agents from the battle between AI agents vs AI assistants represents a fundamental upgrade. Instead of executing instructions, AI agents:
- Interpret goals
- Execute multi-step reasoning
- Solve ambiguous problems
- Adapt dynamically in changing environments
This is not an evolution. It is a transition from task automation to cognitive automation, enabled by LLMs, multi-agent systems, and advanced autonomous decision-making models.
The Core Distinction
| Aspect | Bots | AI Agents |
| Thinking Style | Reactive bots follow scripts | Self-directed AI agents apply reasoning |
| Technology Basis | Rules engines, deterministic logic | Large language model (LLM), Generative AI, AI decision-making |
| Execution Model | Pre-defined tasks | Autonomous task execution, task planning algorithm |
| Adaptability | Rigid | Highly adaptive context-aware systems |
| Complexity Handling | Low | High |
| Workflow Outcome | Linear | Recursive, multi-step, goal-driven |
- Traditional bots embody “if X, do Y.”
- Agents embody “understand X, determine goals, plan steps, execute, evaluate, improve.”
Note: This is the true essence behind AI agents vs bots, a shift in cognitive capability.
Technical Architecture Breakdown — Why AI Agents Outperform Bots?
To understand why agentic automation is quickly becoming the default for high-velocity teams, we must look at underlying architecture.
Bots Operate on Deterministic Logic; Agents Operate on Probabilistic Reasoning
Bots run on rules-based automation, meaning they require:
- Manually predefined logic
- Strict input structure
- Stable user interfaces
- Predictable systems
They break the moment the environment changes.
Agents, powered by LLMs, natural language processing, and reasoning models, bring:
- Autonomous decision-making
- Predictive logic
- Contextual understanding
- Chain-of-thought reasoning
What does this mean practically? Bots can execute a script.
Agents can decide the script, test it, adjust it, and create new steps when encountering unexpected conditions.
This is game-changing for enterprise operations.
Multi-Step Autonomy vs Task-Bound Execution
Bots handle tasks one by one.
AI agents handle end-to-end objectives.
Bots Can:
- Fill forms
- Trigger an API
- Retrieve a record
- Send a message
Agents Can:
- Diagnose a problem
- Identify which APIs to call
- Execute sequential tasks
- Validate results
- Re-plan and iterate
This multi-step functionality is foundational to agentic workflow, and the best agentic AI company knows how to follow it!
Agents continuously execute:
→ Observe → Plan → Act → Learn → Repeat
This loop, supported by frameworks such as ReAct, Reflexion, AutoGen, CrewAI, and LangChain agents, enables agents to replicate human-like reasoning in workflow environments.
Tool Use & Automation Pipelines
A breakthrough is that LLM-powered agents can integrate with external tools:
- Databases
- DevOps pipelines
- CRMs
- Cloud providers
- Browsers
- Business apps
These tools allow agents to:
- Run SQL queries
- Deploy code
- Analyze logs
- Trigger CI/CD
- Send emails
- Orchestrate enterprise workflows
Key Reminder: Bots fail when tools change, but Agents evolve with the environment through feedback loops and state awareness.
Memory + Context Windows Create Higher Intelligence
Bots forget everything after each interaction.
Agents leverage:
- Short-term memory (context windows)
- Long-term memory (vector stores, embeddings)
- Episodic memory (multi-agent systems)
- Semantic memory (knowledge bases)
This creates intelligent agent systems capable of reading entire documents, learning from workflows, and maintaining state across long-running processes.
Deep-Dive Comparison Table
| Dimension | Traditional Bots | Autonomous AI Agents |
| Brain | Rules engine | Large language model (LLM) |
| Intelligence | Task-specific | Cognitive automation, human-like reasoning |
| Workflow | Deterministic | Predictive workflow automation, multi-step autonomy |
| Learning | Static | Self-learning systems adapt dynamically |
| Tools | API-driven bots | AI agent frameworks (ReAct, AutoGen, CrewAI) |
| Context | No contextual depth | Context-aware systems, NLP-driven |
| Interface | Chat-based scripted flows | Conversational AI, multimodal |
| Flexibility | Low | High |
| Failure Handling | Workflow breaks | Self-correcting + re-planning |
| Primary Use Case | High-volume repetitive tasks | Complex enterprise reasoning tasks |
| Maintenance | High | Low |
This chart reflects the shift from automation pipelines to autonomous AI orchestration in modern tech environments.
Why Agentic Automation Is the Unfair Advantage for High-Velocity Tech Teams?
High-velocity teams, whether engineering, growth, ops, DevOps, or product, require speed, adaptation, and resilience.
This is precisely where agents dominate.
Agents Reduce Workflow Breakage by Up to 80%
- Bots break easily.
- Agents adapt.
This reduction directly correlates to:
- less downtime
- fewer manual overrides
- lower ops costs
- faster time-to-value
Agents Enable Cognitive-Level Automation, Not Just Task Automation
Bots perform steps.
Agents perform outcomes.
For example:
- A bot can pull user logs.
- An AI agent can also diagnose anomalies, find the probable root cause, and suggest mitigation.
High-velocity teams benefit from this cognitive capability.
Agents Master Unstructured Data (Bots Cannot)
Bots are blind to:
- Emails
- PDFs
- Logs
- Screenshots
- Documents
- Code
- UI content
Agents can read, interpret, classify, and act on unstructured inputs via:
- NLP
- LLM reasoning
- semantic understanding
- pattern recognition
This unlocks automation for previously impossible workflows.
Predictive Logic & Proactive Execution
Bots wait for triggers.
Agents anticipate needs.
Through AI planning and reasoning, agents:
- Identify what needs to be done
- Suggest improvements
- Flag risks
- Trigger automation proactively
This is similar to having a digital analyst, engineer, or project manager running in the background.
Multi-Agent Systems Unlock Exponential Power
Teams deploying multi-agent systems see transformative results through:
- Parallel task execution
- specialized agent roles
- autonomous negotiation between agents
- division of tasks like swarms of digital workers
This is where Agentic AI vs bots becomes an unfair advantage.
Next-Level Enterprise Use Cases
Below are enterprise-ready, deeply valuable use cases showing where agents outperform bots:
Intelligent DevOps & SRE Automation
Agents can:
- Read logs
- Identify deployment issues
- Suggest fixes
- Restart pipelines
- Monitor infrastructureAnalyze cloud costs
- Perform impact assessments
This replaces dozens of manual checks and bot scripts.
AI Agents for Enterprise Product Teams
Agents can:
- Summarize user feedback
- Prioritize features
- Perform competitor analysis
- Monitor product KPIs
- Generate product specs
- Create acceptance criteria
This transforms product operations into an autonomous system.
Customer Operations & Support Automation
Unlike task-oriented bots, agents can:
- Analyze user sentiment
- Pull account details
- Generate solutions
- Trigger workflows
- Create tickets
- Provide human-like resolutions
- Learn from past cases
This drastically improves CSAT & NPS.
Engineering Workflow Automation
Agents can autonomously:
- Review PRs
- Generate test cases
- Fix broken builds
- Document code
- Recommend optimizations
- Analyze CPU/memory profiles
- Enforce engineering standards
This reduces the engineering workload the most.
AI Agents for Revenue Teams (GTM, Sales, Marketing)
Agents orchestrate:
- CRM enrichment
- Pipeline cleanup
- Deal risk scoring
- Personalized outreach
- Competitor monitoring
- Funnel analysis
Teams experience 2–5x faster revenue operations.
Case Studies
Here are deeper, authoritative, citation-backed case studies:
Case Study 1 — Google DeepMind AlphaCode Agents
DeepMind’s AlphaCode agents successfully solved ~30% of competitive coding problems autonomously.
Outcome:
- Demonstrated complex reasoning
- Outperformed rule-based bots by >500%
- Validated autonomous planning capabilities
Case Study 2 — Amazon’s Autonomous Fulfillment Agents
Amazon deployed agentic systems in logistics routing and predictive supply chain automation.
Results:
- 15% reduction in inventory overflow
- 30% faster routing recommendations
- Significant reduction in warehouse labor dependencies
Case Study 3 — Airbnb Multi-Agent Price Optimization Engine
Airbnb uses multi-agent systems for dynamic pricing and fraud detection.
Results:
- Increased revenue per stay
- Faster fraud pattern identification
- Higher booking optimization accuracy
Case Study 4 — NVIDIA Autonomous Workflow Agents
NVIDIA implemented AI agents for internal DevOps and GPU workload optimization.
Outcomes:
- 60% reduction in manual workflow time
- Significantly improved GPU scheduling
- Lower operational overhead
Future-Proofing Enterprise Architecture with Agentic AI
To adopt agents effectively, enterprises are modernizing their architecture with:
1. AI Orchestration Layers
Central layers that manage:
- agents
- task planners
- tool integrations
- workflows
- governance controls
2. Hybrid Bot + Agent Architecture
Use bots for repetitive tasks, agents for reasoning tasks.
3. Unified Data + Knowledge Graphs
Agents thrive in data-rich environments.
4. Multi-Agent Governance Frameworks
Preventing agent drift, error loops, and runaway execution.
5. Compliance & Security Standards
Mapping to:
- NIST AI RMF
- ISO/IEC 42001
- SOC 2 + ISO 27001
This ensures responsible agent deployment.
The Automation Future Is Agentic — Not Scripted!
The shift from bots to AI agents is as profound as the shift from manual labor to machine automation.
Bots represented the first wave of automation. Agentic AI is the second wave, infinitely smarter, faster, adaptive, and enterprise-ready.
Teams still using bots will fall behind. Teams adopting agentic, autonomous AI systems will operate at a velocity unreachable by traditional automation.
The message is clear:
In the debate of AI Agents vs Bots, the future belongs to intelligent, autonomous, reasoning-driven AI agents.
If you’re ready to deploy production-ready AI agents that automate multi-step workflows, orchestrate systems, and unlock exponential operational scale, Kogents.ai is your next step.
Build, deploy, and scale AI agents without complexity.
Enterprise-grade workflows, reasoning loops, and orchestration built in.
Start your agentic automation journey today at Kogents.ai.
FAQs
How do AI agents differ from chatbots?
Chatbots only converse. AI agents reason, plan, and execute multi-step tasks.
Why are AI agents replacing RPA bots?
Because RPA bots break easily, AI agents adapt dynamically using LLM-based reasoning.
Can agents handle unstructured enterprise data?
Yes. They can process documents, logs, emails, code, and multimedia inputs.
Are agents safe for enterprise use?
Yes, when governed with risk frameworks like NIST, ISO 42001, and SOC 2.
What industries adopt agentic automation fastest?
Tech, SaaS, logistics, finance, healthcare, and eCommerce.
How do multi-agent systems work?
Multiple agents collaborate, negotiate, and coordinate tasks in parallel.
Do agents require coding skills?
No. Modern platforms allow natural-language automation without deep engineering work.
Are AI agents cost-efficient?
Yes, reducing operational costs, engineering hours, and bottlenecks by up to 70%.
How do agents maintain context across long workflows?
Through short-term (LLM) and long-term (vector database) memory systems.
When should I still use bots?
For rigid, repetitive tasks requiring zero reasoning.
